Chemicals From East Palestine Train Disaster Spread to 16 States: Study
Fires after the February 2023 accident caused plumes of toxic chemicals to spread farther than researchers anticipated. "I think we should be concerned," an expert said.
Jun 19, 2024
Toxic chemicals released during fires following the Norfolk Southern train derailment in Ohio last year spread to 16 states and likely Canada, according to a study released Wednesday.
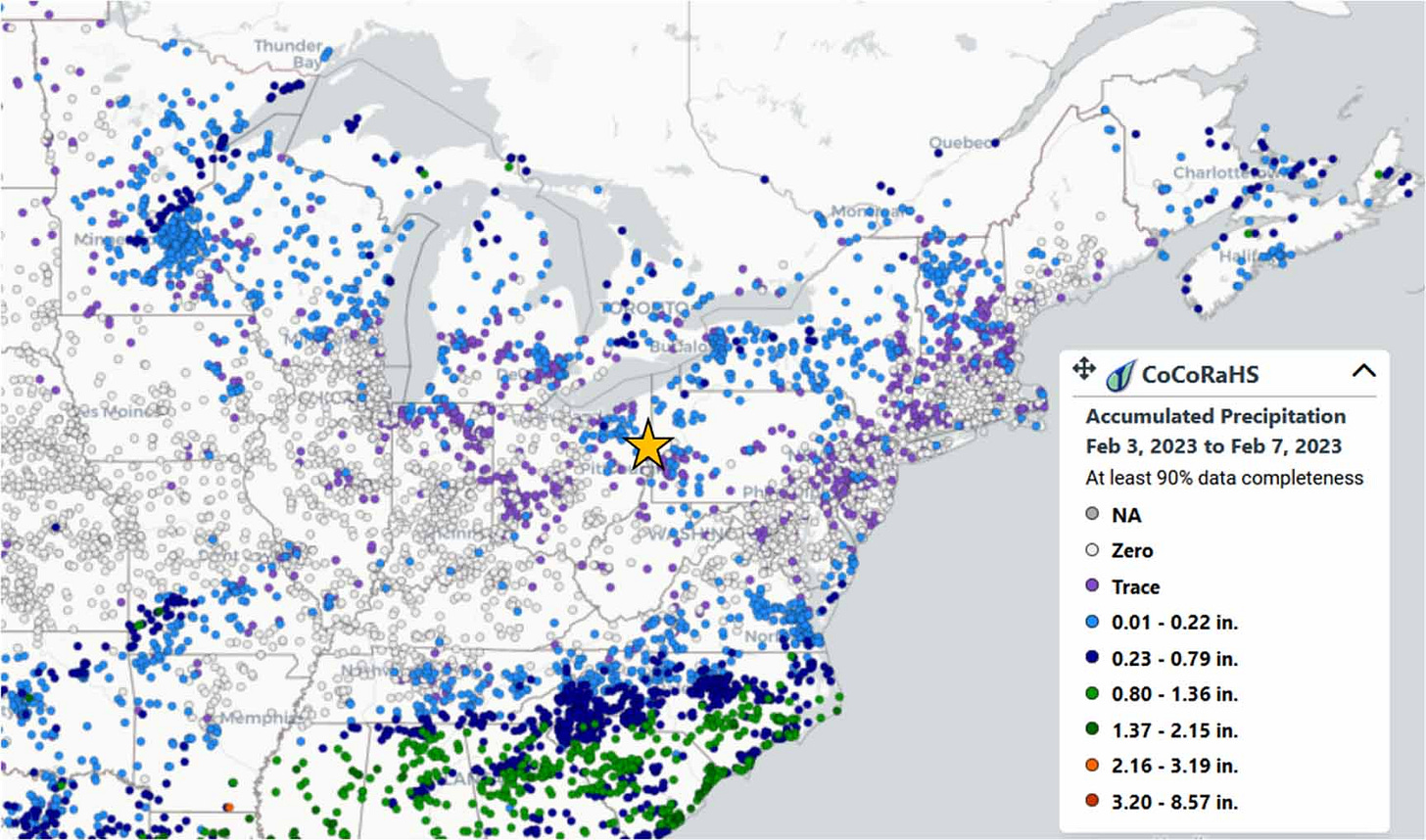
The pollution, some of which came from the burning of vinyl chloride, a carcinogen, spread over 540,000 square miles, showing clearly that "the impacts of the fire were larger in scale and scope than the initial predictions," the authors of the study (re-posted below - jw), published in Environmental Research Letters, found.
Lead author David Gay, coordinator of the National Atmospheric Deposition Program, said that he was very surprised by the way the chemicals had spread. "I didn't expect to see an impact this far out," he told The Washington Post.
Gay said the results did not mean "death and destruction," as concentrations were low on an absolute scale—"not melting steel or eating paint off buildings"—but that they were still "very extreme" compared to normal, with measurements higher than recorded in the previous ten years.
"I think we should be concerned," Juliane Beier, an expert on vinyl chloride effects who didn't take part in the study, told the Post, citing the possibility of long-term environmental impacts on communities.
A Norfolk Southern train crashed in East Palestine, Ohio, a village near the Pennsylvania border and the Appalachian foothills, on February 3, 2023. Dozens of train cars derailed, at least 11 of which were carrying hazardous materials, some of which caught fire after the accident and burned for days. Fearing a large-scale explosion, authorities drained the vinyl chloride from five cars into a trench and set it alight in a controlled burn.
A former U.S. Environmental Protection Agency official later said that the controlled burn went against EPA rules; the head of the National Transportation Safety Board said the deliberate burning was unnecessary.
The local impact of the fires was felt acutely in the month after the accident—a "potent chemical odor hung in the air for weeks," according to The Guardian, and people reported nausea, rashes, and headaches.
The new study helps explain the wider environmental impact. The researchers looked at inorganic compound samples in rain and snow at 260 sites. The highest levels of chloride were found in northern Pennsylvania and near the Canada-New York border, which was downwind from the accident. The authors also found "exceptionally high" pH levels in rain as far away as northern Maine. They did not look at organic compounds such as dioxin or PFAS, which likely also spread following the accident, The Guardian reported. The elevated inorganic chemical levels dropped two to three weeks after the accident.
Norfolk Southern has agreed to pay nearly $1 billion in damages following two settlements reached in recent months. In April, the company reached a $600 million deal with class action plaintiffs living within 20 miles of the derailment site. That deal won't be finalized until the residents officially agree. In May, the company reached a separate $310 million settlement with the federal government. The company has said that it has already spent $107 million on community support and removed the impacted soil.
Norfolk Southern makes billions in profits every year, and the company gave its CEO a 37% pay hike last year, drawing widespread criticism. The company also spent $2.3 million on federal lobbying last year, according to OpenSecrets data reported by Roll Call.
Widespread impacts to precipitation of the East Palestine Ohio train accident
David A Gay1,2, Katelan Blaydes1, James J Schauer1 and Martin Shafer1
Published 19 June 2024 • © 2024 The Author(s). Published by IOP Publishing Ltd
Environmental Research Letters, Volume 19, Number 7
Citation David A Gay et al 2024 Environ. Res. Lett. 19 074022 DOI 10.1088/1748-9326/ad52ac
Abstract
On 3 February 2023, a Norfolk Southern train derailment occurred in East Palestine, Ohio. The accident and subsequent fire resulted in the emissions of large amounts of hazardous compounds to the ambient atmosphere over many days. We used precipitation chemistry measurements routinely collected by the National Atmospheric Deposition Program (NADP) to estimate the spatial extent and chemical compounds deposited as a result of the accident. Our measurements revealed a large areal impact from the Midwest through the Northeast and likely Canada, and perhaps as far south as North Carolina (portions of 16 states, 1.4 million km2). Observations showed the expected high chloride concentrations, but also unexpectedly high pH (basic) and exceptionally elevated levels of base cations exceeding 99th percentiles versus the historic record. These results were consistent with the meteorological conditions and atmospheric trajectories, and were not due to highly-concentrated low volume precipitation samples or wildfires. The robust measurements of the NADP network clearly show that the impacts of the fire were larger in scale and scope than the initial predictions, and likely due to the uplift from the fire itself entraining pollutants into the atmosphere. A more detailed evaluation of the accident and resulting fire could further refine the full impact of the atmospheric concentrations, dry and wet deposition, and the more specific extent of the spatial impact.
1. Introduction
At approximately 9 p.m. on the evening of 3 February 2023, a Norfolk Southern freight train accident occurred in East Palestine Ohio, less than one mile from the Pennsylvania border. About 50 train cars were involved in the accident, of which 38 derailed and at least 11 cars were carrying a variety of hazardous materials. Some of these materials were spilled, and a fire ensued. The subsequent fire burned for a number of days and damaged other cars [1, 2].
The cargo carried by the involved railroad cars included several volatile organic compounds (VOCs), including vinyl chloride, 2-butoxyethanol, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, etc. As the fire continued, authorities attempted to control the fire and the flow of contaminated water, and, as reported, used a small amount of firefighting foams at the scene to control the fire. On 6 February, fire officials conducted what was described as a 'controlled release and burn' of five cars containing vinyl chloride (specifically vinyl chloride monomer, VCM), due to fear of an explosion of one or all of these cars. These cars were breached, the liquid was drained into a trench dug at the scene, and the VCM were set afire and burned. The evacuation order for the surrounding communities was lifted on 8 February, bringing an end to the active fire incident [1].
There were many reports of contaminated water and strong odors during and after the fire. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) began atmospheric monitoring for a number VOCs in and around East Palestine soon after the accident. Significant atmospheric concentrations of many chemicals were measured [3], including relatively high concentrations (>1 µg m−3) of acetone (consistently high), benzene, and other VOCs, and somewhat lower concentrations (>0.1 µg m−3) of ethylbenzene, naphthalene, tetrachloroethene, toluene, and p-xylenes. Table 1 contains a summary of the train's derailed cargo [2]…
Related:
'Reprehensible': NTSB Chair Says Norfolk Southern Interfered With East Palestine Probe
Norfolk Southern Agrees to Pay $600 Million—A Fraction of Its 2023 Profits—for East Palestine Disaster
Biden Announces 'Long Overdue' Rail Safety Rules Despite Industry Objections
'Bombshell' Memo Shows Open Chemical Burn in East Palestine Violated EPA Rules
Norfolk Southern CEO Got a 37% Pay Boost After Toxic East Palestine Crash
Donations (#Value4Value)
Buy Me a Coffee (One time donations as low as $1)
Bitcoin:
bc1qc9ynhlmgxcdd2mjufqr8fxhf248gqee05unmpg (on chain)
thetruthaddict@zeuspay.com (lightning)
Monero:
86X5wSSNL6Q12n4Qjm66vVbNKf5Y481PW3yihDcQ4wcSBNDDxgnNfxb4b8RKWo4fwdXzYFBLp1fYXHZMR6ZEbVmnAQhxdMD
Ways to connect
PGP Fingerprint: 7351 9c62 95cc 8130 d8b1 c877 ec99 9aaf 5b1f b029
Email: thetruthaddict@tutanota.com
Telegram: @JoelWalbert
The Truth Addict Telegram channel
Hard Truth Soldier chat on Telegram
The Truth Addict Media Archive (downloadable documentaries, interviews, movies, TV, stand-up, etc)
Mastodon: @thetruthaddict@noauthority.social
Session: 05e7fa1d9e7dcae8512eed0702531272de14a7f1e392591432551a336feb48357c
Odysee: TruthAddict
Rumble: thetruthaddict09
NoAgendaTube: The Truth Addict





