While the report in this clip is referring specifically to Mexican drug cartels laundering money, it is indicative of the global drug trade and banks in general (see this, this and this for more on banks laundering drug money). If the drug (and contraband) trade actually did stop, the entire global economy would collapse, very likely overnight.
- jw
Drug money as the big banks’ only source of liquidity (2011), clip taken from No Agenda episode 294
Source: Mint Press News
TALIBAN’S MASSIVELY SUCCESSFUL OPIUM ERADICATION RAISES QUESTIONS ABOUT WHAT US WAS DOING ALL ALONG
by Alan MacLeod
The Taliban government in Afghanistan – the nation that until recently produced 90% of the world’s heroin – has drastically reduced opium cultivation across the country. Western sources estimate an up to 99% reduction in some provinces. This raises serious questions about the seriousness of U.S. drug eradication efforts in the country over the past 20 years. And, as global heroin supplies dry up, experts tell MintPress News that they fear this could spark the growing use of fentanyl – a drug dozens of times stronger than heroin that already kills more than 100,000 Americans yearly.
THE TALIBAN DOES WHAT THE US DID NOT
It has already been called “the most successful counter-narcotics effort in human history.” Armed with little more than sticks, teams of counter-narcotics brigades travel the country, cutting down Afghanistan’s poppy fields.
In April of last year, the ruling Taliban government announced the prohibition of poppy farming, citing both their strong religious beliefs and the extremely harmful social costs that heroin and other opioids – derived from the sap of the poppy plant – have wrought across Afghanistan.
It has not been all bluster. New research from geospatial data company Alcis suggests that poppy production has already plummeted by around 80% since last year. Indeed, satellite imagery shows that in Helmand Province, the area that produces more than half of the crop, poppy production has dropped by a staggering 99%. Just 12 months ago, poppy fields were dominant. But Alcis estimates that there are now less than 1,000 hectares of poppy growing in Helmand.
Instead, farmers are planting wheat, helping stave off the worst of a famine that U.S. sanctions helped create. Afghanistan is still in a perilous state, however, with the United Nations warning that six million people are close to starvation.
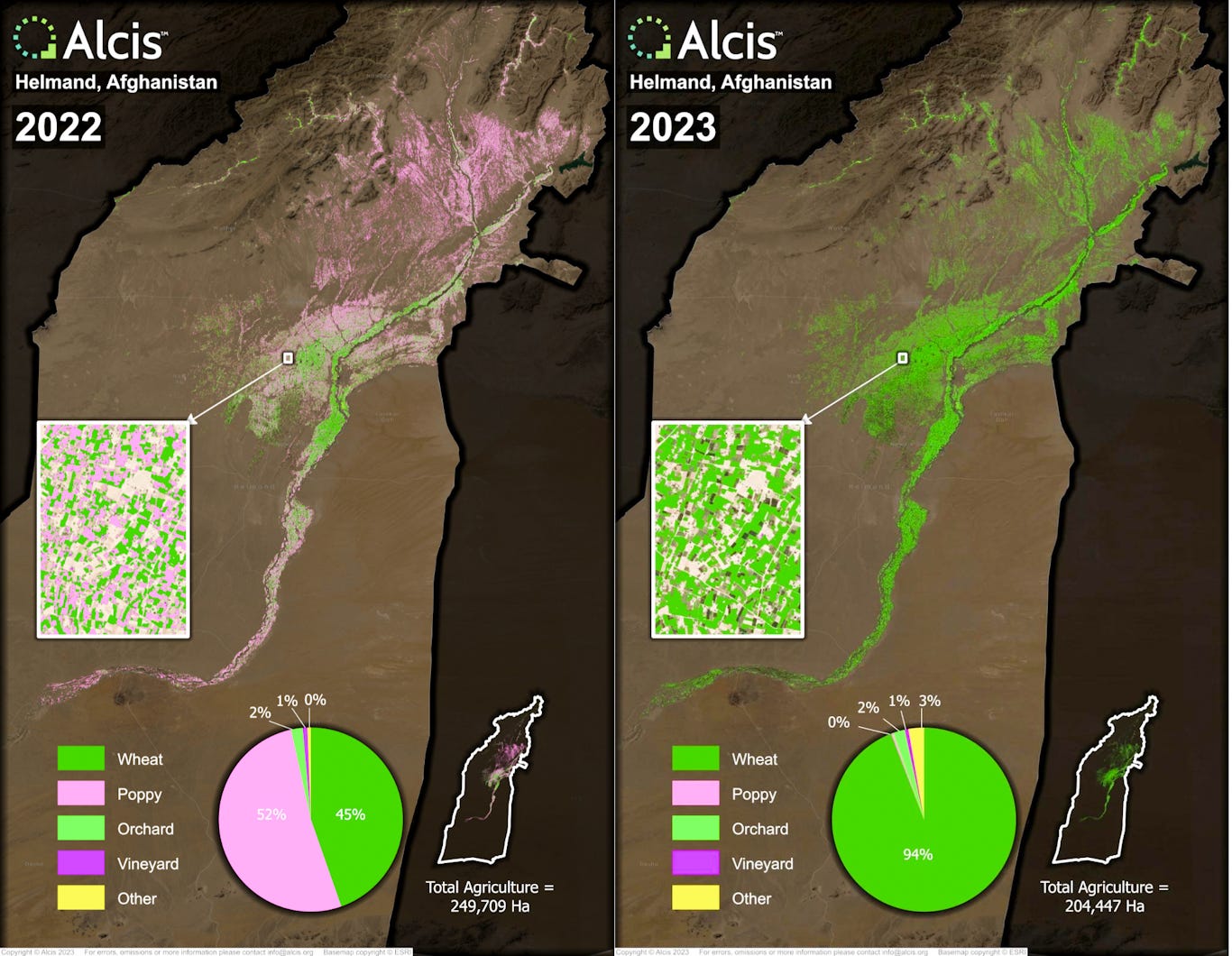
The Taliban waited until 2022 to impose the long-awaited ban in order not to interfere with the growing season. Doing so would have provoked unrest among the rural population by eradicating a crop that farmers had spent months growing. Between 2020 and late 2022, the price of opium in local markets rose by as much as 700%. Yet given the Taliban’s insistence – and their efficiency at eradication – few have been tempted to plant poppies.
The poppy ban has been matched by a similar campaign against the methamphetamine industry, with the government targeting the ephedra crop and shutting down ephedrine labs across the country.
A LOOMING CATASTROPHE
Afghanistan produces almost 90% of the world’s heroin. Therefore, the eradication of the opium crop will have profound worldwide consequences on drug use. Experts MintPress spoke to warned that a dearth of heroin would likely produce a huge spike in the use of synthetic opioids such as fentanyl, a drug the Center for Disease Control estimates is 50 times stronger and is responsible for taking the lives of more than 100,000 Americans each year.
“It is important to consider past periods of heroin shortages and the impact these have had on the European drug market,” the European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA) told MintPress, adding:
Experience in the E.U. with previous periods of reduced heroin supply suggests that this can lead to changes in patterns of drug supply and use. This can include further an increase in rates of polysubstance use among heroin users. Additional risks to existing users may be posed by the substitution of heroin with more harmful synthetic opioids, including fentanyl and its derivatives and new potent benzimidazole opioids.”
In other words, if heroin is no longer available, users will switch to far deadlier synthetic forms of the drug. A 2022 United Nations report came to a similar conclusion, noting that the crackdown on heroin production could lead to the “replacement of heroin or opium by other substances…such as fentanyl and its analogs.”
“It does have that danger in the macro sense, that if you take all that heroin off the market, people are going to go to other products,” Matthew Hoh told MintPress. Hoh is a former State Department official who resigned from his post in Zabul Province, Afghanistan, in 2009. “But the response should not be reinvade Afghanistan, reoccupy it and put the drug lords back in power, which is basically what people are implying when they bemoan the consequence of the Taliban stopping the drug trade,” Hoh added; “Most of the people who are speaking this way and worrying out loud about it are people who want to find a reason for the U.S. to go and affect regime change in Afghanistan.”
There certainly has been plenty of hand-wringing from American sources. “Foreign Policy,” wrote about “how the Taliban’s ‘war on drugs’ could backfire;” U.S. government-funded “Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty” claimed that the Taliban were turning a “blind eye to opium production,” despite the official ban. And the United States Institute of Peace, an institution created by Congress that is “dedicated to the proposition that a world without violent conflict is possible,” stated emphatically that “the Taliban’s successful opium ban is bad for Afghans and the world”.
This looming catastrophe, however, will not hit immediately. Significant stockpiles of drugs along trafficking routes still exist. As the EMCDDA told MintPress:
It can take over 12 months before the opium harvest appears on the European retail drug market as heroin – and so it is too early to predict, at this stage, the future impact of the cultivation ban on heroin availability in Europe. Nonetheless, if the ban on opium cultivation is enforced and sustained, it could have a significant impact on heroin availability in Europe during 2024 or 2025.”
Yet there is little indication that the Taliban are anything but serious about eradicating the crop, indicating that a heroin crunch is indeed coming.
A similar attempt by the Taliban to eliminate the drug occurred in 2000, the last full year that they were in power. It was extraordinarily successful, with opium reduction dropping from 4,600 tons to just 185 tons. At that time, it took around 18 months for the consequences to be felt in the West. In the United Kingdom, average heroin purity fell from 55% to 34%, while in the Baltic States of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, heroin was largely replaced by fentanyl. However, as soon as the United States invaded in 2001, poppy cultivation shot back up to previous levels and the supply chain recommenced.
US COMPLICITY IN THE AFGHAN DRUG TRADE
The Taliban’s successful campaign to eradicate drug production has cast a shadow of doubt over the effectiveness of American-led endeavors to achieve the same outcome. “It prompts the question, ‘What were we actually accomplishing there?!'” remarked Hoh, underscoring:
This undermines one of the fundamental premises behind the wars: the alleged association between the Taliban and the drug trade – a concept of a narco-terror nexus. However, this notion was fallacious. The reality was that Afghanistan was responsible for a staggering 80-90% of the world’s illicit opiate supply. The primary controllers of this trade were the Afghan government and military, entities we upheld in power.”
Hoh clarified that he never personally witnessed or received any reports of direct involvement by U.S. troops or officials in narcotics trafficking. Instead, he contended that there existed a “conscious and deliberate turning away from the unfolding events” during his tenure in Afghanistan.’

Suzanna Reiss, an academic at the University of Hawaii at Manoa and the author of “We Sell Drugs: The Alchemy of U.S. Empire,” demonstrated an even more cynical perspective on American counter-narcotics endeavors as she conveyed to MintPress:
The U.S. has never really been focused on reducing the drug trade in Afghanistan (or elsewhere for that matter). All the lofty rhetoric aside, the U.S. has been happy to work with drug traffickers if the move would advance certain geopolitical interests (and indeed, did so, or at least turned a knowingly blind eye, when groups like the Northern Alliance relied on drugs to fund their political movement against the regime.).”
Afghanistan’s transformation into a preeminent narco-state owes a significant debt to Washington’s actions. Poppy cultivation in the 1970s was relatively limited. However, the tide changed in 1979 with the inception of Operation Cyclone, a massive infusion of funds to Afghan Mujahideen factions aimed at exhausting the Soviet military and terminating its presence in Afghanistan. The U.S. directed billions toward the insurgents, yet their financial needs persisted. Consequently, the Mujahideen delved into the illicit drug trade. By the culmination of Operation Cyclone, Afghanistan’s opium production had soared twentyfold. Professor Alfred McCoy, acclaimed author of “The Politics of Heroin: CIA Complicity in the Global Drug Trade,” shared with MintPress that approximately 75% of the planet’s illegal opium output was now sourced from Afghanistan, a substantial portion of the proceeds funneling to U.S.-backed rebel factions.
UNRAVELING THE OPIOID CRISIS: AN IMPENDING DISASTER
The opioid crisis is the worst addiction epidemic in U.S. history. Earlier this year, Department of Homeland Security Secretary Alejandro Mayorkas described the American fentanyl problem as “the single greatest challenge we face as a country.” Nearly 110,000 Americans died from drug overdoses in 2021, fentanyl being by far the leading cause. Between 2015 and 2021, the National Institute of Health recorded a nearly 7.5-fold increase in overdose deaths. Medical journal The Lancet predicts that 1.2 million Americans will die from opioid overdoses by 2029.
U.S. officials blame Mexican cartels for smuggling the synthetic painkiller across the southern border and China for producing the chemicals necessary to make the drug.
White Americans are more likely to misuse these types of drugs than other races. Adults aged 35-44 experience the highest rates of deaths, although deaths among younger people are surging. Rural America has been particularly hard hit; a 2017 study by the National Farmers Union and the American Farm Bureau Federation found that 74% of farmers have been directly impacted by the opioid epidemic. West Virginia and Tennessee are the states most badly hit.
For writer Chris Hedges, who hails from rural Maine, the fentanyl crisis is an example of one of the many “diseases of despair” the U.S. is suffering from. It has, according to Hedges, “risen from a decayed world where opportunity, which confers status, self-esteem and dignity, has dried up for most Americans. They are expressions of acute desperation and morbidity.” In essence, when the American dream fizzled out, it was replaced by an American nightmare. That white men are the prime victims of these diseases of despair is an ironic outgrowth of our unfair system. As Hedges explained:
White men, more easily seduced by the myth of the American dream than people of color who understand how the capitalist system is rigged against them, often suffer feelings of failure and betrayal, in many cases when they are in their middle years. They expect, because of notions of white supremacy and capitalist platitudes about hard work leading to advancement, to be ascendant. They believe in success.”
In this sense, it is important to place the opioid addiction crisis in a wider context of American decline, where opportunities for success and happiness are fewer and farther between than ever, rather than attribute it to individuals. As the “Lancet” wrote: “Punitive and stigmatizing approaches must end. Addiction is not a moral failing. It is a medical condition and poses a constant threat to health.”
A “UNIQUELY AMERICAN PROBLEM”
Nearly 10 million Americans misuse prescription opioids every year and at a rate far higher than comparable developed countries. Deaths due to opioid overdose in the United States are ten times more common per capita than in Germany and more than 20 times as frequent in Italy, for instance.
Much of this is down to the United States’ for-profit healthcare system. American private insurance companies are far more likely to favor prescribing drugs and pills than more expensive therapies that get to the root cause of the issue driving the addiction in the first place. As such, the opioid crisis is commonly referred to as a “uniquely American problem.”
Part of the reason U.S. doctors are much more prone to doling out exceptionally strong pain medication relief than their European counterparts is that they were subject to a hyper-aggressive marketing campaign from Purdue Pharma, manufacturers of the powerful opioid OxyContin. Purdue launched OxyContin in 1996, and its agents swarmed doctors’ offices to push the new “wonder drug.”

Yet, in lawsuit after lawsuit, the company has been accused of lying about both the effectiveness and the addictiveness of OxyContin, a drug that has hooked countless Americans onto opioids. And when legal but incredibly addictive prescription opioids dry up, Americans turned to illicit substances like heroin and fentanyl as substitutes.
Purdue Pharma owners, the Sackler family, have regularly been described as the most evil family in America, with many laying the blame for the hundreds of thousands of overdose deaths squarely at their door. In 2019, under the weight of thousands of lawsuits against it, Purdue Pharma filed for bankruptcy. A year later, it plead guilty to criminal charges over its mismarketing of OxyContin.
Nevertheless, the Sacklers made out like bandits from their actions. Even after being forced last year to pay nearly $6 billion in cash to victims of the opioid crisis, they remain one of the world’s richest families and have refused to apologize for their role in constructing an empire of pain that has caused hundreds of thousands of deaths.
Instead, the family has attempted to launder their image through philanthropy, sponsoring many of the most prestigious arts and cultural institutions in the world. These include the Guggenheim Museum and the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, Yale University, and the British Museum and Royal Academy in London.
One group who are disproportionately affected by opioids like OxyContin, heroin and fentanyl are veterans. According to the National Institutes of Health, veterans are twice as likely to die from overdose than the general population. One reason for this is bureaucracy. “The Veterans Administration did a really poor job in the past decades with their pain management, particularly their reliance on opioids,” Hoh, a former marine, told MintPress, noting that the V.A. prescribed dangerous opioids at a higher rate than other healthcare agencies.
Ex-soldiers often have to cope with chronic pain and brain injuries. Hoh noted that around a quarter-million veterans of Afghanistan and Iraq have traumatic brain injuries. But added to that are the deep moral injuries many suffered – injuries that typically cannot be seen. As Hoh noted:
Veterans are turning to [opioids like fentanyl] to deal with the mental, emotional and spiritual consequences of the war, using them to quell the distress, try to find some relief, escape from the depression, and deal with the demons that come home with veterans who took part in those wars.”
Thus, if the Taliban’s opium eradication program continues, it could spark a fentanyl crisis that might kill more Americans than the 20-year occupation ever did.
BROKEN SOCIETY
If diseases of despair are common throughout the United States, they are rampant in Afghanistan itself. A global report released in March revealed that Afghans are by far the most miserable people on Earth. Afghans evaluated their lives at 1.8 out of 10 – dead last and far behind the top of the pile Finland (7.8 out of 10).
Opium addiction in Afghanistan is out of control, with around 9% of the adult population (and a significant number of children) addicted. Between 2005 and 2015, the number of adult drug users jumped from 900,000 to 2.4 million, according to the United Nations, which estimates that almost one in three households is directly affected by addiction. As opium is frequently injected, blood-transmitted conditions like HIV are common as well.
The opioid problem has also spilled into neighboring countries such as Iran and Pakistan. A 2013 United Nations report estimated that almost 2.5 million Pakistanis were abusing opioids, including 11% of people in the northwestern province of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Around 700 people die each day from overdoses.
EMPIRE OF DRUGS
Given their history, It is perhaps understandable that Asian nations have generally taken far more authoritarian measures to counter drug addiction issues. For centuries, using the illegal drug trade to advance imperial objectives has been a common Western tactic. In the 1940s and 1950s, the French utilized opium crops in the “Golden Triangle” region of Southeast Asia in order to counter the growing Vietnamese independence movement.
A century previously, the British used opium to crush and conquer much of China. Britain’s insatiable thirst for Chinese tea was beginning to bankrupt the country, seeing as China would only accept gold or silver in exchange. The British, therefore, used the power of its navy to force China to cede Hong Kong to it. From there, it flooded mainland China with opium grown in South Asia (including Afghanistan).
The effect of the Opium War was astonishing. By 1880, the British were inundating China with more than 6,500 tons of opium per year – the equivalent of many billions of doses. Chinese society crumbled, unable to deal with the empire-wide social and economic dislocation that millions of opium addicts brought. Today, the Chinese continue to refer to the period as the “century of humiliation”.
Meanwhile, in South Asia, the British forced farmers to plant poppy fields instead of edible crops, causing waves of giant famines, the likes of which had never been seen before or since.
And during the 1980s in Central America, the United States sold weapons to Iran in order to fund far-right Contra death squads. The Contras were deeply implicated in the cocaine trade, fuelling their dirty war through crack cocaine sales in the U.S. – a practice that, according to journalist Gary Webb, the Central Intelligence Agency facilitated.
Imperialism and illicit drugs, therefore, commonly go together. However, with the Taliban opium eradication effort in full effect, coupled with the uniquely American phenomenon of opioid addiction, it is possible that the United States will suffer significant blowback in the coming years. The deadly fentanyl epidemic will likely only get worse, needlessly taking hundreds of thousands more American lives. Thus, even as Afghanistan attempts to rid itself of its deadly drug addiction problem, its actions could precipitate an epidemic that promises to kill more Americans than any of Washington’s imperial endeavors to date.
Feature photo | Illustration by MintPress News
Alan MacLeod is Senior Staff Writer for MintPress News. After completing his PhD in 2017 he published two books: Bad News From Venezuela: Twenty Years of Fake News and Misreporting and Propaganda in the Information Age: Still Manufacturing Consent, as well as a number of academic articles. He has also contributed to FAIR.org, The Guardian, Salon, The Grayzone, Jacobin Magazine, and Common Dreams.
Source: Global Research
What Spearheaded 22 Years of War and Atrocities? Unocal and the Coveted Trans-Afghan Pipeline Route
By Larry Chin
This incisive and carefully researched article by Larry Chin was originally published by Global Research in March 2002 under the title: Unocal and the Afghanistan Pipeline
October 7, 2023 marks the commemoration of the US – NATO invasion of Afghanistan on October 7, 2001.
Twenty-two Years of War and Atrocities have been spearheaded by
the geopolitics of the strategic trans-Afghan pipeline, which is the object of this article,
the Taliban’s decision (2000) to drastically curtail opium production with a view to cancelling outright the multibillion Afghan drug trade.
September 11, 2001 provided the justification to wage war on Afghanistan. A war cabinet was created at 11 o’clock at night on September 11, 2001. On the following day, NATO’s North Atlantic Council met in Brussels.
An unnamed foreign power had attacked America allowing the nation under attack, to strike back in the name of “self-defense”.
“if it is determined that the [September 11, 2001] attack against the United States was directed from abroad [Afghanistan] against “The North Atlantic area“, it shall be regarded as an action covered by Article 5 of the Washington Treaty”. (emphasis added)
The bombing and invasion of Afghanistan which commenced on October 7, 2001 was described as a “campaign” against “Islamic terrorists”, rather than a war.
America’s “War on Terrorism” was born on September 11, 2001.
Michel Chossudovsky, August 30, 2023
***
After the fall of the Soviet Union, Argentine oil company Bridas, led by its ambitious chairman, Carlos Bulgheroni, became the first company to exploit the oil fields of Turkmenistan and propose a pipeline through neighboring Afghanistan. A powerful US-backed consortium intent on building its own pipeline through the same Afghan corridor would oppose Bridas’ project.
The Coveted Trans-Afghan Route
Upon successfully negotiating leases to explore in Turkmenistan, Bridas was awarded exploration contracts for the Keimar block near the Caspian Sea, and the Yashlar block near the Afghanistan border. By March 1995, Bulgheroni had accords with Turkmenistan and Pakistan granting Bridas construction rights for a pipeline into Afghanistan, pending negotiations with the civil war-torn country.
The following year, after extensive meetings with warlords throughout Afghanistan, Bridas had a 30-year agreement with the Rabbani regime to build and operate an 875-mile gas pipeline across Afghanistan.
Bulgheroni believed that his pipeline would promote peace as well as material wealth in the region. He approached other companies, including Unocal and its then-CEO, Roger Beach, to join an international consortium.
But Unocal was not interested in a partnership. The United States government, its affiliated transnational oil and construction companies, and the ruling elite of the West had coveted the same oil and gas transit route for years.
A trans-Afghanistan pipeline was not simply a business matter, but a key component of a broader geo-strategic agenda: total military and economic control of Eurasia (the Middle East and former Soviet Central Asian republics). Zbigniew Brezezinski describes this region in his book “The Grand Chessboard-American Primacy and Its Geostrategic Imperatives” as “the center of world power.” Capturing the region’s oil wealth, and carving out territory in order to build a network of transit routes, was a primary objective of US military interventions throughout the 1990s in the Balkans, the Caucasus and Caspian Sea.
As of 1992, 11 western oil companies controlled more than 50 percent of all oil investments in the Caspian Basin, including Unocal, Amoco, Atlantic Richfield, Chevron, Exxon-Mobil, Pennzoil, Texaco, Phillips and British Petroleum.
In “Taliban: Militant Islam, Oil and Fundamentalism in Central Asia” (a definitive work that is a primary source for this report), Ahmed Rashid wrote,
“US oil companies who had spearheaded the first US forays into the region wanted a greater say in US policy making.”
Business and policy planning groups active in Central Asia, such as the Foreign Oil Companies Group operated with the full support of the US State Department, the National Security Council, the CIA and the Department of Energy and Commerce.
Among the most active operatives for US efforts: Brzezinski (a consultant to Amoco, and architect of the Afghan-Soviet war of the 1970s), Henry Kissinger (advisor to Unocal), and Alexander Haig (a lobbyist for Turkmenistan), and Dick Cheney (Halliburton, US-Azerbaijan Chamber of Commerce).
Unocal’s Central Asia envoys consisted of former US defense and intelligence officials. Robert Oakley, the former US ambassador to Pakistan, was a “counter-terrorism” specialist for the Reagan administration who armed and trained the mujahadeen during the war against the Soviets in the 1980s. He was an Iran-Contra conspirator charged by Independent Counsel Lawrence Walsh as a key figure involved in arms shipments to Iran.
Richard Armitage, the current Deputy Defense Secretary, was another Iran-Contra player in Unocal’s employ. A former Navy SEAL, covert operative in Laos, director with the Carlyle Group, Armitage is allegedly deeply linked to terrorist and criminal networks in the Middle East, and the new independent states of the former Soviet Union (Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Kyrghistan).
Armitage was no stranger to pipelines. As a member of the Burma/Myanmar Forum, a group that received major funding from Unocal, Armitage was implicated in a lawsuit filed by Burmese villagers who suffered human rights abuses during the construction of a Unocal pipeline. (Halliburton, under Dick Cheney, performed contract work on the same Burmese project.)
Bridas Versus the New World Order
Much to Bridas’ dismay, Unocal went directly to regional leaders with its own proposal. Unocal formed its own competing US-led, Washington-sponsored consortium that included Saudi Arabia’s Delta Oil, aligned with Saudi Prince Abdullah and King Fahd. Other partners included Russia’s Gazprom and Turkmenistan’s state-owned Turkmenrozgas.
John Imle, president of Unocal (and member of the US-Azerbaijan Chamber of Commerce with Armitage, Cheney, Brezezinski and other ubiquitous figures), lobbied Turkmenistan’s president Niyazov and prime minister Bhutto of Pakistan, offering a Unocal pipeline following the same route as Bridas.’
Dazzled by the prospect of an alliance with the US, Niyazov asked Bridas to renegotiate its past contract and blocked Bridas’ exports from Keimar field. Bridas responded by filing three cases with the International Chamber of Commerce against Turkmenistan for breach of contract. (Bridas won.) Bridas also filed a lawsuit in Texas charging Unocal with civil conspiracy and “tortuous interference with business relations.” While its officers were negotiating with Pakistani and Turkmen oil and gas officials, Bridas claimed that Unocal had stolen its idea, and coerced the Turkmen government into blocking Bridas from Keimir field. (The suit was dismissed in 1998 by Judge Brady G. Elliott, a Republican, who claimed that any dispute between Unocal and Bridas was governed by the laws of Turkmenistan and Afghanistan, rather than Texas law.)
In October 1995, with neither company in a winning position, Bulgheroni and Imle accompanied Niyazov to the opening of the UN General Assembly. There, Niyazov awarded Unocal with a contract for a 918-mile natural gas pipeline. Bulgheroni was shocked. At the announcement ceremony, Unocal consultant Henry Kissinger said that the deal looked like “the triumph of hope over experience.”
Later, Unocal’s consortium, CentGas, would secure another contract for a companion 1,050-mile oil pipeline from Dauletabad through Afghanistan that would connect to a tanker loading port in Pakistan on the coast of the Arabian Sea.
Although Unocal had agreements with the governments on either end of the proposed route, Bridas still had the contract with Afghanistan.
The problem was resolved via the CIA and Pakistani ISI-backed Taliban. Following a visit to Kandahar by US Assistant Secretary of State for South Asia Robin Raphael in the fall of 1996, the Taliban entered Kabul and sent the Rabbani government packing.
Bridas’ agreement with Rabbani would have to be renegotiated.
Wooing the Taliban
According to Ahmed Rashid, “Unocal’s real influence with the Taliban was that their project carried the possibility of US recognition, which the Taliban were desperately anxious to secure.”
Unocal wasted no time greasing the palms of the Taliban. It offered humanitarian aid to Afghan warlords who would form a council to supervise the pipeline project. It provided a new mobile phone network between Kabul and Kandahar. Unocal also promised to help rebuild Kandahar, and donated $9,000 to the University of Nebraska’s Center for Afghan Studies. The US State Department, through its aid organization USAID, contributed significant education funding for Taliban. In the spring of 1996, Unocal executives flew Uzbek leader General Abdul Rashid Dostum to Dallas to discuss pipeline passage through his northern (Northern Alliance-controlled) territories.
Bridas countered by forming an alliance with Ningarcho, a Saudi company closely aligned with Prince Turki el-Faisal, the Saudi intelligence chief. Turki was a mentor to Osama bin Laden, the ally of the Taliban who was publicly feuding with the Saudi royal family. As a gesture for Bridas, Prince Turki provided the Taliban with communications equipment and a fleet of pickup trucks. Now Bridas proposed two consortiums, one to build the Afghanistan portion, and another to take care of both ends of the line. By November 1996, Bridas claimed that it had an agreement signed by the Taliban and Dostum—trumping Unocal.
The competition between Unocal and Bridas, as described by Rashid, “began to reflect the competition within the Saudi Royal family.”
In 1997, Taliban officials traveled twice to Washington, D.C. and Buenos Aires to be wined and dined by Unocal and Bridas. No agreements were signed.
It appeared to Unocal that the Taliban was balking. In addition to royalties, the Taliban demanded funding for infrastructure projects, including roads and power plants. The Taliban also announced plans to revive the Afghan National Oil Company, which had been abolished by the Soviet regime in the late 1970s.
Osama bin Laden (who issued his fatwa against the West in 1998) advised the Taliban to sign with Bridas. In addition to offering the Taliban a higher bid, Bridas proposed an open pipeline accessible to warlords and local users. Unocal’s pipeline was closed—for export purposes only. Bridas’ plan also did not require outside financing, while Unocal’s required a loan from the western financial institutions (the World Bank), which in turn would leave Afghanistan vulnerable to demands from western governments.
Bridas’ approach to business was more to the Taliban’s liking. Where Bulgheroni and Bridas’ engineers would take the time to “sip tea with Afghan tribesmen,” Unocal’s American executives issued top-down edicts from corporate headquarters and the US Embassy (including a demand to open talks with the CIA-backed Northern Alliance).
While seemingly well received within Afghanistan, Bridas’ problems with Turkmenistan (which they blamed on Unocal and US interference) had left them cash-strapped and without a supply.
In 1997, they went searching for a major partner with the clout to break the deadlock with Turkmenistan. They found one in Amoco. Bridas sold 60 percent of its Latin American assets to Amoco. Carlos Bulgheroni and his contingent retained the remaining minority 40 percent. Facilitating the merger were other icons of transnational finance, Chase Manhattan (representing Bridas), Morgan Stanley (handling Amoco) and Arthur Andersen (facilitator of post-merger integration). Zbigniew Brezezinski was a consultant for Amoco.
(Amoco would merge with British Petroleum a year later. BP is represented by the law firm of Baker & Botts, whose principal attorney is James Baker, lifelong Bush friend, former secretary of state, and a member of the Carlyle Group.)
Recognizing the significance of the merger, a Pakistani oil company executive hinted, “If these (Central Asian) countries want a big US company involved, Amoco is far bigger than Unocal.”
Clearing the Chessboard Again
By 1998, while the Argentine contingent made slow progress, Unocal faced a number of new problems.
Gazprom pulled out of CentGas when Russia complained about the anti-Russian agenda of the US. This forced Unocal to expand CentGas to include Japanese and South Korean gas companies, while maintaining the dominant share with Delta.
Human rights groups began protesting Unocal’s dealings with the brutal Taliban. Still riding years of Clinton bashing and scandal mongering, conservative Republicans in the US attacked the Clinton administration’s Central Asia policy for its lack of clarity and “leadership.”
Once again, violence would change the dynamic.
In response to the bombing of US embassies in Nairobi and Tanzania (attributed to bin Laden), President Bill Clinton sent cruise missiles into Afghanistan and Sudan. The administration broke off diplomatic contact with the Taliban, and UN sanctions were imposed.
Unocal withdrew from CentGas, and informed the State Department “the gas pipeline would not proceed until an internationally recognized government was in place in Afghanistan.” Although Unocal continued on and off negotiations on the oil pipeline (a separate project), the lack of support from Washington hampered efforts.
Meanwhile, Bridas declared that it would not need to wait for resolution of political issues, and repeated its intention of moving forward with the Afghan gas pipeline project on its own. Pakistan, Turkmenistan and Afghanistan tried to push Saudi Arabia to proceed with CentGas (Delta of Saudi Arabia was now the leader). But war and US-Taliban tension made business impossible.
For the remainder of the Clinton presidency, there would be no official US or UN recognition of Afghanistan. And no progress on the pipeline.
Then George Walker Bush took the White House.
Featured image is from Fabius Maximus Website
The original source of this article is Global Research
Copyright © Larry Chin, Global Research, 2023
Waging devestation. Masquerading as justice against those who are truly victims of the installation that politically numbs and nullifies, or other wise entraps a population with repressive legislation. From Humboldt County to Zero Tolerance, an inference can be made: the War on Drugs is a war on us. How can we begin to see the reality when the CIA sells us our dreams in the street? You're not burning rebellion when your melting your mind. You're just a model citizen in their eyes. Too discouraged to see the truth...to jaded to even care. Government pushing in, Government cracking down. Cracking down on the very epidemic they helped create to preoccupy the dissatisfied. The situation is very clear. The same pockets are getting filled, the same people are getting jailed. Covert operations never seen or heard by American senses. Funded by the dirty hands of greed... their international drug scheme. Its all for the same cause. Benefiting the same corporations that dare to drug screen for jobs. Reject the CIA, reject their drugs...
Ways to connect
Telegram: @JoelWalbert
Email: thetruthaddict@tutanota.com
The Truth Addict Telegram channel
Hard Truth Soldier chat on Telegram
Mastodon: @thetruthaddict@noagendasocial.com
Session: 05e7fa1d9e7dcae8512eed0702531272de14a7f1e392591432551a336feb48357c
Odysee: TruthAddict
Donations (#Value4Value)
Buy Me a Coffee (One time donations as low as $1)
Bitcoin:
bc1qe8enf89g667dy890j2lnt637xqlt9wvc9f07un (on chain)
nemesis@getalby.com (lightning)
joelw@fountain.fm (lightning)
+wildviolet72C (PayNym)
Monero:
43E8i7Pzv1APDJJPEuNnQAV914RqzbNae15UKKurntVhbeTznmXr1P3GYzK9mMDnVR8C1fd8VRbzEf1iYuL3La3q7pcNmeN








The connection between banking and drug money is titanium-strength. In hindsight, knowing as we do there is no actual connection between Afghanistan and 9/11 yet the occupation used the 'attack' as the justification for the replacement of the anti-drug Taliban. Who benefits? Who decides? Tragic, horrific, immoral... I lack words adequate to express my anger and grief at our inability to end war on Earth.