Dig It! #202: Space: The New Frontier For The Central Control Grid - Special Report
Link to video version on Rumble
Source: Corey’s Digs.
Space: The New Frontier For The Central Control Grid
by Corey Lynn
October 6, 2023
What if you had the ability to construct the central operation center for the entire control grid from a location with no real jurisdiction and no accessibility or oversight? What if the massive power source you need to run this operation could be harnessed under the guise of “climate change” in an expedited manner? And, what if you could have full surveillance and weaponry at your disposal with an entire financial infrastructure in place whose data sits in the palm of your hand while you control the levers?
This report will show how the central infrastructure for the all-seeing, all-assets control grid is being built, a giant leap with the digital currency agenda, and cites over 160 pieces of evidence:
Brush Strokes: Important Stats and Dates of Significance
Deloitte’s Financial Services Industry Predictions
Space: The New Frontier for The “All Assets” and Surveillance Control Grid
The Data: Space-Based Data Centers
The Power Supply: Space-Based Solar Systems
The Vehicle: Satellites
The Tool: Blockchain
The Surveillance and Weaponry: Space Fence
The Safe Zone: Space Laws
Giant Leap: Digital Currency Moving Faster Than a Rocket
T-minus
Download this full report from the Bookshop in PDF format.
Watch Dig It! #202 for Corey’s breakdown of this report.
Is it possible that Elon Musk’s military-backed operation is sending up thousands of satellites to help people gain internet access from remote areas? Why not? Getting everyone plugged in plays a key role in the grand plan, and affords the strategically placed satellites the opportunity for their intended use while building a whole other set of satellites alongside them to capture all the data. Is it possible that the U.S. Space Fence, the world’s most advanced radar surveillance system, is really in place for monitoring debris in the atmosphere for everyone’s safety? Sure, it provides excellent cover for all forms of surveillance and weaponry. Are countries working diligently to bring space-based solar systems to outer space so as to beam a 24/7 power source down to earth in order to power towns and save the world from the dangers of “climate change.” Don’t be ridiculous. Sabotaging the oil supply and fossil fuels has worked out spectacular for strategically placing solar systems in space to power the satellites that will control the grid. It’s genius. Are they eagerly trying to build cargo rockets to transport people to colonize Mars, millions of miles away? Uh, that’s a one-way ticket everyone should pass on.
The best part of having a massive power source is to be able to fire up the space-based data systems and expedite the financial control grid that much faster. After all, digital currency, blockchain, and tokenization require an endless supply of power to run. As the battle over currency is moving at full throttle, much is happening behind the scenes to bring the digital world to life, and it doesn’t seem as though CBDCs will be necessary for the master plan to lock into place – at least not immediately. Banks will be the driving force to bring everyone into the age of QR codes, biometrics, and tokenization.
Why? Because a digital identity that links to your financials, personal information, healthcare, education, bills, utility usage, purchases, and movement, coupled with a social credit score, leaves a lot at stake floating out in the ether under “their” control. Who is “they?” “They” are named and documented throughout countless reports on Corey’s Digs. Many players are involved. Here’s a good start.
This report will help show what is transpiring in space, the digital currency trajectory, the central control grid, and how it all connects. It will reveal key statistics and dates that show elements of how it came to be, the pace at which this is moving, and some stunning “coincidences.” It will become very apparent that this is a global goal that all countries are engaged in, and whereas each country wants to maintain a middle management position over their own population, it is clear that each uses the UN and their agendas as “cover,” each is moving toward a digital currency, and each move on this battlefield will have a ripple effect for all across the entire world.
James Fitzgerald recently published an article titled Sky’s the Limit for Globalists’ Boiling Earth Narrative on Corey’s Digs, which gives an excellent overall bird’s eye view of how satellites are playing a much larger role in the development of agriculture, environmental, and the technological control grid. It is recommended reading as a foundation for this report.
Before diving into this, it’s important to pause, observe, and recognize the incredible lengths they are going to try to have full control over the population and all assets. In the process of trying to demoralize everyone, they have become overtly transparent which has created a rift in some of their plans. Whereas they have every intention of moving forward despite this rift, there are some agendas that cannot be achieved without mass compliance. Feeding too much energy, and especially belief, into them reaching their goals actually fuels that reality forward, while speaking out against their agendas and defining them as a false future reality can actually limit their forward movement. It’s a balancing act and they know the game well, hence why they use fear to draw people’s energy in. For these reasons it’s important not to validate the power they believe they have over every individual, but rather acknowledge the absurdity and danger of their desired outcome and affirm that you refuse to be a part of it or comply with it, while focusing energy into a positive future reality that we would all like to manifest together.
Brush Strokes: Important Stats and Dates of Significance
Note: These are snippets of very relevant information, many of which are not included in the overall report, so be sure to review all of these.
• The global population is allegedly now over 8 billion as of 2023, despite the enormous excess death totals coming out from different countries.
• There are currently over 4.9 billion social media users globally which is expected to reach 5.85 billion by 2027. China ranks first, followed by India and the U.S. All major social media platforms monetize and/or charge fees for benefits, linking people’s financials to these platforms.
• There are over 6.4 billion mobile phone users (the weapon of choice) as of 2022 which is expected to reach 7.7 billion by 2028, and 85% are currently utilizing social media from their phones.
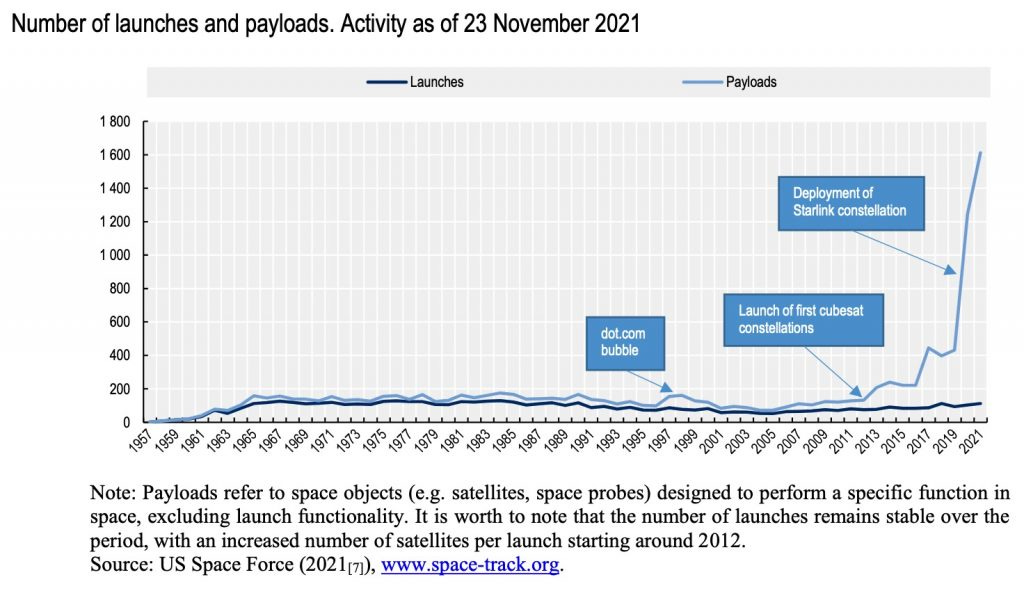
• According to the UN Office for Outer Space Affairs, 11,330 satellites are orbiting space as of June 2023. In 2022, the largest amount of satellites and cubesats launched into space in one year, at 2,474. To put this in perspective, between 1957 and 2018, the combined number of satellites launched is less than the five years between 2019 and 2023. It is increasing exponentially, with a 53.84% increase in communications satellites, 13.30% increase in earth observation satellites, and 7.53% increase in technology development/demonstration satellites since January 2022. The U.S. outpaces every other country by nearly eight times the number of satellites in space, with China, the United Kingdom, and Russia following behind. That being said, one could pull up information from multiple different sources and get entirely different numbers. According to Slingshot Aerospace, who is in the process of expanding their ground-based optical telescopes and sensors around the world, they expect there to be between 60,000 and 150,000 satellites orbiting by the end of the decade.
• Morgan Stanley’s space team estimates that the $350+ billion global space industry will reach over $1 trillion by 2040.
• The International Space Station (ISS) is being decommissioned in 2030 and replaced with 4 “commercial destination” space stations, providing they all succeed in their build outs.
• The WEF has already established the Global Future Council on The Future of Space and developed the world’s first Space Sustainability Rating system (SSR) for space missions to reduce debris in a global space economy that is rapidly growing. They created four levels of certifications for satellite manufacturers and launch service providers. Of course, all major companies, including SpaceX and Lockheed Martin are on board with this. After all, the climate change agenda makes for great cover for space operations and surveillance. On September 28, 2023, they published an article titled “These are the space missions to look out for in the 2020s,” which encompasses missions to the Moon, Mars, Mercury, and NASA’s upcoming mission to Saturn in 2026, as well as document previous missions including India’s recent alleged landing on the Moon’s south pole in August. Saturn is only 746 million miles away at its closest point, but who’s counting.
• In order to pull off a full digital currency system with blockchain, it would require populations to reduce their energy usage by 1/3rd because it is a massive power source drain. However, space-based solar systems to power satellites where the control grid would operate, could dramatically minimize the need to reduce power on earth while expediting the control grid in space. The United States, Russia, European Space Agency, China, Saudi Arabia, Australia, Japan, and the United Kingdom are already working on their space-based solar systems. More on this below.
• In 2019, President Trump signed Space Policy Directive-4, ordering the Pentagon to establish the Space Force as the sixth branch of the U.S. military.
• On December 9, 2020 President Trump issued the 2020 National Space Policy, replacing the 2010 version, with a goal of working with commercial and international partners, generating new markets and entrepreneurship, and leaving a permanent human presence on the Moon, Mars, and beyond.
• “Fast Payment Systems” was rolled out in January 2021, by the World Bank with Bill Gates’ help, and is already running in over 60 countries.
• In March 2022, the Biden administration issued an Executive Order on “Ensuring Responsible Development of Digital Assets,” which placed “the highest urgency on research and development efforts into the potential design and deployment options of a United States CBDC.”
• On September 16, 2022, the Biden administration released the first-ever comprehensive framework for responsible development of digital assets.
• The Biden administration stated, “The global renewable energy market is projected to be worth $2.15 trillion by 2025.”
• The top 10 digital payment companies by revenue are: JP Morgan Chase & Co., Visa Inc., PayPal Holdings Inc., Mastercard Incorporated, Fisery Inc., Stripe, Intuit Inc., Global Payments Inc., ACI Worldwide Inc., and PayU.
• A number of establishments provide “reverse ATMs,” known as cash-to-card kiosks, so that people can voluntarily feed their hard cash into the machine and get a debit card, in preparation to move people off cash. Various companies are partnering up to make these options more readily available. Yet, some states have passed laws banning companies from being “cash free” to their customers, which of course has spurred the rise of establishments putting in reverse ATMs. See how that works? The final stage of this goal is to convert cash into a virtual card that goes on your smartphone.
• According to Juniper Research, the number of QR code scan-to-pay users will exceed 2.2 billion in 2025, up from 1.5 billion in 2020, which equates to 29% of all mobile phone users worldwide in 2025.
• In China, QR code payments reached $1.3 trillion U.S. in the fourth quarter of 2019. According to CNN, $1.65 trillion was spent in 2016 for the entire year in China. Globally, 4% of all consumer transactions utilize a QR code, and that is expected to start soaring. An enormous amount of banks, digital payment companies, and corporations have already incorporated QR codes into transactions, which can currently store data up to 7,089 numeric characters or 4,269 alphanumeric characters.
• The Federal Reserve has created a QR code work group under the “Faster Payments Council” to develop a QR code interface for faster and instant payment transactions across various payment systems and rails, and to facilitate adoption and usage of faster payments. They produced a 19-page white paper on it in July 2022. They want a “standardized certification program covering all major mobile devices and operating systems” and “extensible standards with the ability to offer value-added services such as merchant offers, coupons and tokenization.”
• ISO 20022, the standards for financial messaging, was developed in 2004 by the International Organization for Standardization, and launched in March 2023. Hundreds of banks and corporations have already begun migration but have until 2025 to fully migrate. The biggest benefit of these new standards allows for much larger data that can flow through payments across any use, capital markets, e-invoicing, and cards, while the format can support structured and unstructured data.
• The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications (SWIFT), a member-owned cooperative headquartered in Belgium with a system that is run by the central banks of the G10 countries, the European Central Bank, and National Bank of Belgium, developed the MyStandards web-based application to manage ISO messaging standards and market practices in 2012, with the recent upgrade for ISO 20022 having launched in March 2023, which has already been adopted by 70 countries.
• In March 2023, the IMF released their report on cash and digital currency, drawing data from 14 advanced and emerging market economies. They concluded that the trend in cash use for payments is falling for half of the world’s population. They stated, “such a measure can help inform policy decisions regarding CBDCs and regulatory decisions concerning access to and use of cash.”
• The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) published their ‘Blueprint for the future monetary system: improving the old, enabling the new’ on June 20, 2023 which Corey’s Digs reported on. The BIS’ blueprint proposes that all private property in the real world, such as money, houses, cars, etc., would be “tokenised” into digital assets within an “everything in one place” global unified ledger. CBDCs would be “core to the functioning” of this tokenised world and serve as the reserve currency on the unified ledger. Transactions between CBDCs and tokenised assets, which represent real-world assets, would operate seamlessly through smart contracts on one programmable platform. Each token representing a real-world asset in this digital space would contain a large amount of data received from the real world in real time about what it is, who it belongs to, etc., as well as rules on how that particular asset can and cannot be used. The BIS explains how these rules are set up by “directly embedding supervisory features into the token itself, which can be tailored to specific rules.
• FedNow (payment gateway through the Federal Reserve) began its pilot in the U.S. in July, 2023 through 35 banks and credit unions, plus service providers and the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Bureau of the Fiscal Service.
• Deloitte released their predictions on the financial services industry on July 31, 2023. When Deloitte offers “predictions,” it’s important to pay attention because it is essentially part of their game plan. See the breakdown below.
• On September 9, 2023, the G20 publicly agreed to build the enslavement system, with new international governance for artificial intelligence and a “Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)” to include digital identification, payment infrastructure and data exchange all under the guise of “improving lives” and enabling “digital inclusion.”
Their “declaration” also includes India’s plan to build a Global Digital Public Infrastructure Repository (GDPIR), which consists of a virtual repository of DPI to be shared by G20 members “and beyond.”
The 37-page Declaration includes just about everything a “conspiracy theorist” needs for receipts on long-proven theories. They provide a plethora of documents annexed to the Declaration beginning on page 30. From health to education, the climate hoax, digital infrastructure, and financial control, they rolled it all in here. Their Sustainable Development Goals are best broken down in Corey’s Digs 17 Goals Toward Enslavement.
Deloitte’s “Financial Services Industry Predictions” is Revealing
On July 31, 2023, Deloitte released their report on “Financial Services Industry Predictions.” Deloitte is a key globalist player who often collaborates with the WEF. For example, their white paper on “A Blueprint for Digital Identity: The Role of Financial Institutions in Building the Digital Identity,”released in August 2016, stated that financial institutions should drive the creation of digital identity systems, disrupt the credit bureau model, blur the lines between financial and non-financial advisory, and bring in biometrics. Corey’s Digs covered this in the report on vaccine ID passports. In this current paper, they “predict” the following:
• Deloitte estimates “the revenue for alternative data providers, earned from all industries globally with the majority coming from investment management firms, to grow 29x between 2022 and 2030. The new data largely consist of novel types and forms of data such as satellite images, social media posts, geolocation data, credit card transactions, and mobile application data that are starkly different from the traditionally structured financial data.”
• Deloitte states that banks will develop more advanced biometric security systems due to an increase in cybercriminals, and because of the increasing importance for digital currencies such as CBDCs. They give an example of the European Union’s work and explain that by expanding these verification systems it will not only provide safeguards with banking, but will also confirm a user’s identity when sharing medical data, taking online exams, or making age-restricted purchases. Deloitte is so confident about the expansion of biometrics, they estimate that in just a few short years “three billion global consumers are expected to make US$5.1 trillion of purchases using biometric payments.” It should be noted that biometrics is one area Twitter/X is moving toward for those who wish to have a blue checkmark as well as plug into the ad revenue stream.
• Deloitte says that consumers will “increasingly use their wallets to help fight climate change with carbon-offset purchases.” They “predict” that carbon offsets will be embedded in many purchasing decisions such as through travel, ordering food, or “negotiating a new mortgage rate,” and that it will become so pervasive it will reach a US$100 billion market by 2030. Just as in their earlier report about banks being instrumental in rolling out a digital ID, they want banks pushing carbon credits as well. “Banks could be instrumental in developing and supporting the back-end infrastructure that connect brands’ payment processes to the carbon credit market. And banks can play an instrumental role in developing and supporting the carbon credit market.”
• Deloitte also estimates “advancements in self-driving technology may eliminate the need for around 380,000 long-haul truck drivers in the next five years.”
Based on the bullet points under “Brush Strokes” above, in addition to the complete breakdown tying the financial movement together, further down in this report, it would seem that Deloitte is once again on target. It would also seem that they can build the control grid before CBDCs even come into play. More on that below.
Space: The New Frontier for The “All Assets”and Surveillance Control Grid
“We’re really talking about something which is, in the long term, like rebuilding the internet in space.” – Elon Musk said during a speech in Seattle
The top 10 largest space and exploration companies in the world are Boeing, SpaceX, Raytheon, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Astra, Virgin Galactic, and General Dynamics, and boy oh boy are they busy.
The OECD published a paper in November 2022 titled “A new landscape for space applications: Illustrations from Russia’s war of aggression against Ukraine.” They stress the growing importance of space technologies and digitalization, expanding commercialization, and the need for government space investments, while addressing data, infrastructure, vulnerabilities, international cooperation, and the war’s impact.
Satellites store and move data, blockchain is making its way into this data, the digital financial system is accelerating, space fence is surveilling, space-based solar and data systems are being constructed, and the laws (or lawlessness) of running this full operation in space is on their side, which coincides perfectly with the many immunities and privileges that central banks and numerous organizations already enjoy.
Imagine running a control grid from space, complete with global surveillance, the ability to generate 24/7 power, to hold and store all data, to manipulate the weather and atmosphere, to have weapons that can pulse frequencies to alter behaviors or incinerate blocks instantly with directed energy weapons. Just imagine.
It’s all out on the table and the competition is palpable. Certain countries are aligning, as allies are critical to maintaining control over their own country and its population. The financial sector is chomping at the bit. While the central banks set the pace and give marching orders, all of the digital wallet and crypto companies are striving to be on top. Everyone wants a piece of the pie, and their eyes are on space. Elon Musk would like X to be the “everything app” where users can tap into “their entire financial world” on a platform he hopes will run “half of the global financial system.” Who better connected than to pull this off with the military while people continue to raise him up as a hero of “free speech” and give him their financial digits for ad revenue to make his dream a reality? Even if it means providing a government ID along with biometrics that will soon be linked to a QR code one day. And even though many of these individuals are aware that Linda Yaccarino serves as the chair of the WEF’s Future of Work task force, was brought on by Elon to be Twitter/X’s CEO, recently announced they will be censoring “lawful but awful” behavior, they continue to make money for Twitter/X to build the enslavement system. Would it make a difference if they knew that the ads they are promoting is much of legacy media, Disney, transgender shows, and Amazon – all places that push false narratives for control over people, plus Disney’s rap sheet of pedophiles?
It will “simplify things for people.” COOL. He’s just… so cool. Wake up. In addition to this report, here’s a little more history on Elon Musk:
Elon, X, and the Epitome of a Front Man (link to Rumble)
On August 28, 2023, Elon Musk’s Twitter Payments LLC received another approved license in the state of Rhode Island for processing cryptocurrency payments, bringing the total number of states to seven. Whereas Musk recently stated that he will never create a cryptocurrency, it’s clear that he plans to accept crypto and there is much anticipation as to whether it will be Dogecoin, Bitcoin, XRP, or others.
Despite people’s belief that Elon Musk is trying to prevent WWIII and won’t allow the U.S. government to utilize his satellites for battle and nefarious actions, nothing could be further from the truth. Over three years ago, in April 2020, SpaceX teamed up with the Air Force to link Starlink satellites with multiple armed forces systems for a huge live fire exercise that included ground forces, submarines, ships, and other space-based assets, to shoot down a cruise missile and a drone. Prior to that, Starlink satellites connected with a Lockheed Martin AC-130 gunship. SpaceX has teamed up with the Department of Defense on many payloads and projects, and other live fire exercises.
The ultimate goal was to build the new Advanced Battle Management System (ABMS) to allow for the coordination of U.S. forces and allies in real-time across land, sea, air, and space, with this new system being equipped with artificial intelligence. The Department of Defense has a new strategy to ensure control over space, which includes utilizing small satellites and space-based capabilities that are unknown to the public and competitors.
“If you get ABMS right, you’ve just built the military’s ‘internet of things’,” stated William Roper, then-Air Force acquisition chief.
By December 2022, SpaceX unveiled Starshield, a “secured satellite network for government entities.” This entails sensors, custom-built spacecraft, and secure communications via Starlink satellites. “Because of the rapidly improving commercial space capabilities, a comprehensive plan for using commercial space systems in the context of classified U.S. space capabilities is needed,” said Heidi Shyu, undersecretary of defense for research and engineering, in a memo on November 21, 2022. One of the goals is to build a low earth orbit tracking layer of missile-detection satellites, whereby a mesh network will move data.
Ukraine was a great test market for Starlink, which is what the Pentagon was hoping for. Everything else was theater. SpaceX sent over 22,000 Starlink satellites to Ukraine and replenished any that were destroyed in combat. In December 2022, Congress passed the 2023 spending bill with a hefty sum of over $69 billion for the DoD, including $1.7 billion for Space Force programs.
Musk’s SpaceX isn’t the only game in town, but it is certainly a key one. Obviously Boeing, Raytheon, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Astra, Virgin Galactic, and General Dynamics play a big role, in addition to numerous tech companies. More on this below.
The Data: Space-Based Data Centers
Morgan Stanley’s space team estimates that the $350+ billion global space industry will reach over $1 trillion by 2040.
Thanks to Hewitt Packard’s HPE Spaceborne Computer-2, the first edge computing data center is already operational in space, with AI capabilities. Astronauts can run their DNA analysis in 13 minutes right on the International Space Station (ISS), along with the DNA of rodents or plants. The goal is to expand on satellite-to-satellite communications, work related to 5G, and build computer systems that can be commercialized and attached to satellites, with the ultimate goal of the capability to process space data in space by 2027. Once they achieve that, space-based data centers will be able to handle the workloads for earth-based customers. Several companies are already working on space-based data centers. Rick Ward, founder and CTO at OrbitsEdge said that in addition to the plan of servers being in satellites, the ISS, and the new commercial space stations, he expects to see them on the Lunar Gateway space station, the Moon, and Mars.
Once again, space-based data centers are needed because of the power consumption and pollution that is creating “climate change caused by humans.” According to the University of Quebec’s College of Technology (Canada), data centers account for 10% of global energy consumption and “4% of the greenhouse gases produced by human activity.” Just as with the space-based solar systems, numerous companies and countries also have their sites set on space-based data systems.
The European Union, for example, has teamed up with Thales Alenia Space with a goal of deploying data centers in Earth orbit by the early 2030s under their Advanced Space Cloud for European Net Zero (ASCEND) emissions and data sovereignty program. Yves Durand, director of technology at Thales Alenia Space is working with top experts in space infrastructure, including Carbone 4, VITO, Orange, CloudFerro, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, ArianeGroup, DLR, and Airbus Defense and Space.
Multiple articles on space-based data centers all point to space providing a cooler environment, less energy usage, and no vibration. They also state that quantum computing is ideal for this environment and that neural network computing and financial data centers will require this high processing capacity.
The Power Supply: Space-based Solar Systems
“It appears to be only a matter of time before power beaming is used to move energy to address critical challenges facing our world, and beyond.” – Paul Jaffe, Principal Investigator in the Spacecraft Engineering Department of the United States Naval Research Laboratory
In 1977, NASA was already talking about space-based solar systems replacing fossil fuels after the idea was proposed by aerospace engineer Peter Glaser in the 1960s. In September 2021, the UK commissioned a report on space-based solar systems that showed it’s technically feasibly and economically competitive. The report claims that space-based solar power could generate up to 10GW of electricity a year by 2050, accounting for a quarter of the UK’s current electricity usage. Two months later, the Financial Times published a video showing a visual presentation on how space-based solar systems could be deployed in 10 years, claiming these massive microwaves would not be carcinogenic, and could power millions of homes. They even talk about how the energy could be pointed toward any country to provide power, costing half as much as electricity generated from earth, and those owning this infrastructure could then technically sell the power to any country. Gosh, wouldn’t it be fun if that became the main power source and they just cut the beam whenever they wanted? It’s more likely a cover story to power the control grid in Space.
According to the European Space Agency, who has full immunities and privileges, high-earth orbiting satellites would gain ten times more energy from the sun compared to systems on the ground.
Beyond Earth Institute, a think tank with hard hitters who work to change policies, published a “National Strategy for Space Solar Power” in August 2021, suggesting that space solar power can not only power the world, but power worlds beyond as well, and that America should take the lead. They claim that space solar power yields up to 40 times greater sunlight access than ground solar systems.
Satellites are powered by solar panels and lithium ion batteries. In the case of Starlink satellites, they typically orbit for five years before they reach end of life, at which point they are allegedly steered into earth’s orbit to burn up. They claim that this will alleviate any debris in orbit, but one can’t help but wonder what that will look like once they reach their goal of 42,000 satellites orbiting, in addition to the military’s and all other satellites.
According to NASA, typical research satellites run with only 200 to 800 watts of electricity which is generated through solar cells and stored in batteries.
The argument being made by satellite and tech companies, space agencies, and governments, is that we are in such a climate crisis that we must implement data centers in space as well as draw energy from the sun while in space and beam it down to earth. It’s a great cover story. While some make it sound like this would be the expedited way to do it, which would give them their space control grid, others argue that we need both – solar in space and on land. This of course is to continue to capitalize on the industry on the earth plane, while also setting policies and regulations that destroy industries and people so that the space control grid can rule.
Countries Already Building The Infrastructure
• In March 2023, the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory launched Space Wireless Energy Laser Link (SWELL), the first laser power beaming experiment demonstrated in space. This is part of the U.S. Department of Defense’s Space Test Program H9 mission carried out from the International Space Station. Launched aboard the SpaceX Dragon, they intend to carry out several experiments in a yearlong mission to collect data. By utilizing laser transmitters and photovoltaic receivers, they established power beaming links, meaning they were able to deliver energy through electromagnetic waves instantly. They claim this is safe and can be used to distribute power on the moon, other places in space, and eventually to earth from satellites. By July they reported that they had surpassed 100 days of successful on-orbit laser operations.
• In June 2023, the UK announced funding for several research initiatives, including Cambridge University who will develop super lightweight solar panels for satellites and a group at Queen Mary University of London are developing a wireless system to beam the solar power from space to earth, while others are working on showing how solar energy from space can feed the power grid on earth to help achieve Net Zero.
• The European Space Agency is set to complete their commercial-scale space-based solar power plants by the end of 2023 to test them out and gather information by the end of 2025. Their goal is to test radio frequency, lasers, and reflecting sunlight down to solar farms on the ground.
• China already has a ground-based wireless power transmission test facility in place that it intends to test out in 2028.
• Britain and Saudi Arabia have teamed up to build a solar energy station in space with the hopes of completing it by 2035.
• In Australia, Solar Space Technologies is working on building a space-based solar system. In fact, they partnered with Mankins Space Technologies out of the U.S. to build the SPS Alpha that was examined for the report commissioned by the UK.
• Japan has big plans to build their space-based solar power and next-generation solar cells by 2025. Once again, they want to launch satellites and equip them with solar panels to generate power back to earth. They state that each satellite will generate 1 million kW of electricity, equivalent to the output of a nuclear power plant and that they produce 10 times more power than ground-based solar panels. To be clear, they are beaming electromagnetic waves like those used in telecommunications and microwave ovens.
In addition to this, They have developed flexible solar cells called perovskite solar cells to expand an area to retrieve the power, such as on exterior walls of buildings.
• Russia has long been planning to build satellites that would beam energy from space and provide electricity for their cities on earth, as far back as 1985 when it was still the Soviet Union. Scientists began working on a project called “Star Electricity” that they hoped would be completed within 15 years. The project entailed building a power plant in outer space working on solar energy. In this old NYT article from 1987, some experts were concerned that birds might be harmed by repeatedly flying through microwave beams. Of course nowadays, that sentiment has been dropped. Curious. Fast forward to 2022 when the Russian Space Agency Roscosmos announced its completion of their solar space power plant (SKES) project. The goal is to provide a charging station in space while also providing electricity to remote locations on earth through laser beams to a ground-based system with mobile antennas. No reports were found to indicate when it’s going up in space.
• The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) just announced it is launching India’s first space-based solar observatory called Aditya-L1 to study the sun, physics of the solar corona, magnetic field topology, and coronal mass ejections.
It’s clear that there is a race to provide power in space, but they may just carry out some of these “power beams” to earth as a new money laundering industry and for cover. One question is, how will all of these electromagnetic waves and lasers impact airlines, birds, or people? More concerning is whether these electromagnetic beams could come with a host of mind-altering frequencies?
The Vehicle: Satellites
Countries operating satellites as of 2020:
Satellites play the most important role in building out the control grid.
The “Communications Satellite Act of 1962,” known as the Comsat Act, authorized U.S. participation in an international cooperation agreement between telecommunication agencies in 18 nations, proposed by the U.S., on a satellite communications network known as Intelsat so that each nation could access portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. In 1969, Intelsat was the organization who transmitted television images of the alleged Apollo 11 moon landing. Here’s a little more history on Intelsat, ECHELON, and more. This intergovernmental consortium was privatized when in March 2000, Congress passed the Orbit Act requiring both Intelsat and Inmarsat to be transformed into privately held for-profit corporations to “promote a competitive market.” In July 2001, Intelsat transferred its satellite and financial assets to Intelsat Ltd., and til this day remains one of the largest satellite service providers. Two months later was the tragic event of 9/11. After bombing Afghanistan, instead of exercising “shutter control” the Pentagon spent millions buying exclusive rights to Ikonos satellite pictures. The following year, in March 2002, SpaceX was born.
Elon Musk’s Starlink runs under SpaceX with ambitious goals of having 42,000 satellites in orbit in the near future. Starlink was created in 2014 with its first successful launch on November 11, 2019. They typically launch about 60 satellites at a time, which can be seen as a train of lights across the sky. Starlink currently already has over 4,500 satellites in orbit which can be viewed in real time on this map. It is reported that Starlink is currently the largest satellite constellation in space. SpaceX is reported to have launched the first 5G satellite in low-earth orbit on April 15, 2023.
Starlink satellites have the capability to beam lasers to one another and create a sort of mesh network transfer of data. They are already hovering in over 60 countries. They have over 140 ground base stations for beaming data to satellites, with over 60 in the U.S. alone. SpaceX’s sister company, SpaceX Services, Inc., was granted a blanket license for the operation of up to one million end-user customer earth stations. In April, they filed for a “blanket license” with the FCC to be able to add as many “earth stations” as needed throughout the entire U.S. and international waters worldwide, without having to file for a license at each location as they have previously done. This request includes being able to deploy vehicle-mounted earth stations, plus earth stations on vessels, aboard aircraft, and in motion.
SpaceX’s Starshield satellite division was revealed in December 2022. According to the web page, “Starshield leverages SpaceX’s Starlink technology and launch capability to support national security efforts. While Starlink is designed for consumer and commercial use, Starshield is designed for government use.” It’s about “national security.” It goes on to say, “Starshield uses additional high-assurance cryptographic capability to host classified payloads and process data securely.”
Now pay attention to this next bit. “Starlink’s inter-satellite laser communications terminal, which is the only communications laser operating at scale in orbit today, can be integrated onto partner satellites to enable incorporation into the Starshield network.” Consumers > Data > Starlink > Starshield > Big Gov and DOD.
Elon Musk’s X.AI and TruthGPT are just getting started with transforming people in ways they can’t even begin to imagine yet, and it plays directly into the transhumansim agenda.
Amazon is hoping to get half of their FCC approved satellites in orbit by 2026. Amazon’s internet will be comprised of 3,236 satellites by the time they pull this off.
Though this next tidbit isn’t about satellites, it certainly may have a bearing on them or somehow play a role in this bigger scheme, so it seemed worthy of including in this report. On August 8, 2023, Breakthrough Energy, Google and American Airlines teamed up to allegedly change the course of airlines’ flight patterns to avoid producing contrails that contribute to climate change. According to Breakthrough Energy’s web page, they are saying that a recent IPCC report, contrails account for 35% of aviation’s global warming impact. No mention of “chemtrails,” just contrails. See the con? So what did they do? They allegedly combined satellite imagery, weather and flight path data, and used AI to develop contrail forecast maps in order to test if pilots can actually choose routes that avoid creating contrails. So I have to ask – what are they really trying to avoid, why are they needing to change flight patterns, and can this literally be done “on the fly?”
The Tool: Blockchain
“Blockchain will provide outer space with an immutable and automated information ledger. Until the end of the time, the transaction is there and tamper-proof.” – Blockchain for Space Governance, Tony Blair Institute for Global Change
They can’t possibly build space-based data centers powered by space-based solar systems that are juicing satellites to keep the flow of data moving to special government-owned satellites without incorporating blockchain to maintain a record and run the world’s tokens of every single asset, including humans, now can they?
In the 2022 “Blockchain for Space Governance” paper published by the Tony Blair Institute for Global Change, they stress the following points:
“Blockchain is a disruptive technology that unlocks new business models for space activities. Depending on the blockchain application, new business models such as fractionalisation and tokenisation of space assets can be unlocked. For an industry with a constant need for heavy funding, blockchain can be leveraged for raising capital through crowdfunding from token sales, an approach that highlights the fact that space belongs to everyone.
Several features of blockchain technology, such as the fact that it is distributed (not tied to a single jurisdiction), immutable (tamper-resistant), transparent (trackable due to immutable audit trail), autonomous (relying on consensus algorithms rather than sovereign entities), alegal (existing outside the concept of law), and automated (programmable: code could be law), make it a viable candidate for adoption in space governance.”
Who better to test this out than J.P. Morgan? After all, they launched Onyx in 2020 to create the world’s first bank-led blockchain platform. That same division thought it might be fun to test it out in space and created SpaceBridge to show how a blockchain-based satellite-to-satellite payment would work. Watch the demo here. J.P. Morgan announced that they tested the world’s first bank-led tokenized value transfer in space, executed via smart contracts on a blockchain network established between satellites orbiting the earth. The announcement states that “space exploration is becoming increasingly well-funded and presents an exciting opportunity to deploy financial technology to create a brand-new payments infrastructure leveraging blockchain.”
But J.P. Morgan isn’t the only thug on the “block” working on building this infrastructure. Here is just a brief snapshot of some others:
NASA
In 2020 NASA solicited for the development of blockchain that could enhance operational efficiency for managing distributed space missions, among other things. NASA put together an early research paper illustrating the role and capabilities of blockchain usage within constellation and swarm satellite architectures, showing the use of smart contracts, distributed ledger, data exchanges, and logging and tracking of command and control events. It is a fairly detailed breakdown described in an easy to understand manner, worth taking a look at.
NASA maintains daily summaries upon the ISS. On December 7, 2022, their daily report included the following:
“NanoRacks Module-83 was installed into NanoRacks Mainframe Alpha. Module-83 is a simple Plug-n-Play tech demo to test the usability of SpaceChains multi-signature security system as well as reliability of GOMSpace boards within the ISS environment. SpaceChain 2.0 validates the hardware and software needed for blockchain transactions between hardware on the ground and the space station. Relaying transactions to the space station protects them from physical attack, while multi-signature technology and secure satellite transmission provide more security from cyberattacks. The investigation also actively explores what types of space payloads could use blockchain.”
SpaceChain
SpaceChain declares that they are the world’s leading integrator of space, security, and blockchain. SpaceChain was recently founded in 2017 as a private company by Jeff Garzik, Nick Trudgen, and Zee Zheng, with headquarters in Singapore and regional offices in the UAE and UK. That said, in August 2022, SpaceChain announced that they were bringing on Cliff Beek as their new CEO to lead the global expansion and establish a global headquarters in the U.S. The lead investors are Google for Startups and the European Space Agency, followed by Eureka Network, Innovate UK, and Enterprise Singapore, and Beek will be focused on securing more investments.
Cliff Beek’s former position was CEO of Cloud Constellation Corporation, who is also covered in this report, below. His goal is to expand SpaceChain’s product line of customized space nodes, smart contracts, digital asset transactions, and the integration of blockchain-enabled payloads onto satellite constellations. By November 2022, SpaceChain had launched its second Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) payload, making it SpaceChain’s seventh blockchain payload into space on the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. This included the integration of Velas which is said to be the world’s fasted EVM blockchain handling 50,000+ transactions per seconds. Installing it on the ISS via NanoRacks allows it to send Velas digital assets from space, including VLX, tokens and NFTs, and also incorporates smart contracts and coin minting.
SpaceChain has an extensive 2023 document on the synergy of blockchain and space and why it’s needed, including a timeline of their involvement since their inception in 2017, space nodes, multisignature wallet service, and a myriad of satellite-based applications. They emphasize security, open-source, and decentralization throughout. One thing they point out is that they have “developed a mobile device that lets you perform digital asset transactions for Bitcoin, Ethereum, and stablecoin at any time and anywhere, allowing you to connect to a network anywhere you are. No ground infrastructure is needed as it communicates directly with satellites.”
IBM Space Tech
IBM has long been involved with NASA and space. Just this year IBM partnered with NASA to “build an AI model that could speed up the analysis of satellite images and boost scientific discovery,” in the name of climate change. They are working to make this “model” public through Hugging Face, an open-source AI platform. IBM Space has partnered with Cloud Constellation, and more recently Ubotica for space AI applications, reducing the dependence on ground systems, Edge Computing in Space, blockchain for supply chains for space tech, deploying satellites, etc. Naeem Altaf, IBM’s CTO for SpaceTech says that government and financial applications will utilize space blockchain first, quickly followed by other industries.
“Eventually, deep space will become part of the national security strategy and blockchain will play a valuable role in making sure that data is secure and not compromised.” – Dennis Gatens, CCO of Cloud Constellation
Blockstream & Bitcoin
Blockstream was the first to launch a satellite that could distribute Bitcoin blockchain, back in 2017. “While our core satellite network is designed to distribute the bitcoin blockchain, we’ve also enabled service where anybody can send any data they want via our satellite network and then pay for it in bitcoin,” stated Chris Cook, CTO of Blockstream.
Cryptosat
In January 2023, Cryptosat launched its second “cryptographically-equipped” satellite, called Crypto2, carried by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 which was also carrying 114 satellites for multiple global operators. Crypto1’s goal, launched in May last year, was to provide blockchain applications, and Crypto2 was to provide additional computational power.
Cryptosat’s co-founder Yan Michalevsky said “there is a lot of need for this … If we’re looking into protocols, especially in Web3, there are whole financial systems and smart contract systems, kind of like digital legal agreements that depend on the trustworthiness of the cryptography behind it.”
China
In July 2023, China’s Tai’an Star Era 16 launched as the first ever satellite to carry a blockchain imaging and screening system into orbit. The blockchain system is referred to as ADAChain and was developed by NationStar Aerospace Technology Co. with the capabilities of on-orbit visual blockchain multi-signature authentication, video visual broadcasting, and visual remote sensing data storage certificate confirmation. It is allegedly for the use of obtaining spectral information on agriculture, water resource management, investigating mineral resources, environmental monitoring, and emergency safety.
Deloitte
Deloitte has their eyes on space as well. Why wouldn’t they? They’ve been a champion of blockchain and digital assets for years. In fact, on September 12, 2023 Deloitte announced it’s strategic alliance with Bitwave to “revolutionize asset accounting and compliance.” By using Bitwave’s software that has the capability of automating the flow of data from over 70 blockchains and decentralized finance systems into ERP systems, combined with Deloitte’s accounting, tax and governance, and risk expertise, they can provide services to companies who utilize digital assets. This will streamline crypto payments, automate accounting, and of course adjust for taxes while being compliant on a global level. Not to get too off topic but Patrick White, the co-founder and CEO of Bitwave, once enjoyed a BBQ at Bill Gates’ home when interning at Microsoft. That was his most “interesting story” that happened to him since he began his career, when asked the question in an interview.
When it comes to outer space, Deloitte says that they “strive to be the go-to professional services organization for commercial entities and government organizations involved in space.” They have already advised “space-focused organizations across multiple government sectors, including defense, intelligence, and civilian, as well as more than 85% of the Fortune 500” and consider themselves to be “the world’s first professional services practice devoted to supporting the entire space value chain.”
Deloitte’s two papers titled “A Space Perspective: Tech Trends 2019” and “The Commercialization of Low Earth Orbit” 2023, provide further insight into their assessment on the future of Space. Here are a few cliff notes:
• Working in concert, techniques and capabilities such as computer vision, conversational voice, auditory analytics, and advanced augmented reality and virtual reality can transform the ways we engage with machines, data, and each other.
• Advanced global connectivity can extend AI, image recognition, facial recognition, and other tools into the field.
• Learn from the use of AI, Blockchain, digital transformation, and more in other industries to manage and secure the tsunami of data.
• The Air Force’s use of the Space Enterprise Consortium (SpEC) provides a new and faster way to procure prototypes and capabilities with non-traditional industry partners that will accelerate use of digital transformation technology.
• The creation of a portfolio architect for space acquisition and systems development represents a new way to remove silos and approach transformation for the long run.
Deloitte, SpaceX, big Gov, and others like to tempt everyone with “human spaceflight,” “trips to Mars and the Moon,” and nifty “space elevators,” when it’s a manipulation tactic to distract people from the true agenda. They are glamorizing Space as the new Hollywood and everyone gets to be a star in their own movie. “Millions watched the return of human spaceflight from U.S. soil on commercial vehicles, private astronaut missions are gaining traction, and a variety of potentially game-changing vehicles are being designed and tested. Coverage across news, streaming, and social platforms has once again thrust human space exploration to the forefront of the public eye,” stated Deloitte in their 2023 paper. That’s the plan – to keep everyone’s eyes on the movie instead of the documentary rolling out.
Did U.S. astronauts actually land on the moon back in 1969? It’s a viable question. The moon is allegedly over 238,000 mi from the earth on average, while the average distance to Mars is 140 million miles. The alleged upcoming 2026 mission to Saturn is a mere 746 million miles from earth, on its closest day. Aside from vast distances, there is an astronomical amount of radiation to combat, hence one of NASA’s issue with going beyond low earth orbit today. See here, and here.
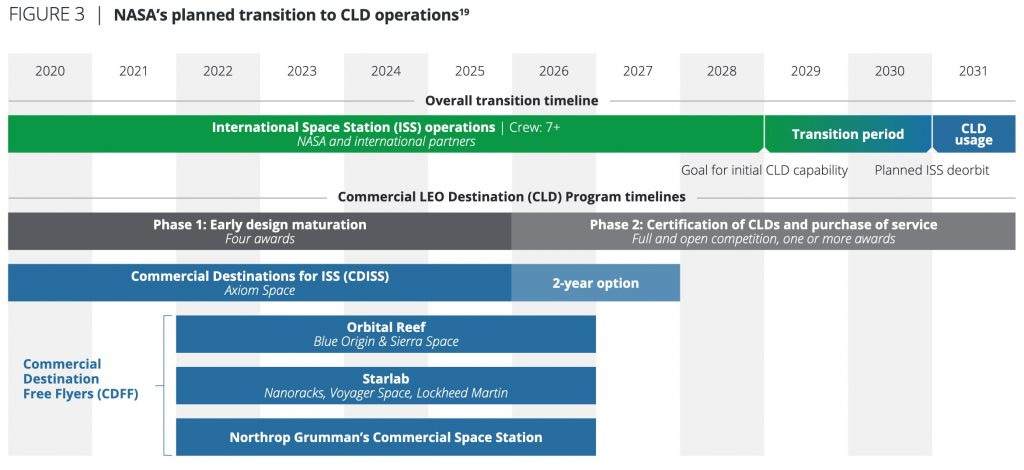
The said goal is to decommission the International Space Station (ISS) in 2030 and create new commercial space stations. NASA awarded up to $140 million to Axiom Space and a combined $415 million to Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin, NanoRacks, and Northrop Grumman to phase in new commercial destinations by 2030. They would like four commercial space stations with Blue Origin and Sierra Nevada’s “Sierra Space” to build out “Orbital Reef,” NanoRacks, Voyager Space, and Lockheed Martin to build out “Starlab,” Northrop Grumman to build its commercial space station, and ISS to act as a commercial destination until it’s phased out.
Surely, 2030 is just a coincidence. And, don’t get your hopes up for space tourism because they’ve warned that only 1 or 2 of these commercial space stations for human and cargo travel to the Moon and Mars will succeed. Plus, it’s going to take billions to make this all happen. It’s a good thing they’ve swept trillions under the rug to save up for this endeavor.
Besides, one space industry leader has already made it clear that “humans are the weakest link in space exploration.”
The Surveillance and Weaponry: Space Fence
What is Space Fence? According to Lockheed Martin, it is the world’s most advanced radar. It is the second generation space surveillance system to track space debris in earth’s orbit as well as satellites, and is operated by the U.S. Space Force. As with all “solutions,” an issue arose back in 2009 when two communications satellites collided, causing a large amount of Space debris, which of course required immediate action to expand on the surveillance network with an upgraded system having the capabilities to zero in on much smaller debris at 10 times the amount of the previous system, by utilizing S-band radar. The original system had been transferred from the U.S. Navy to the U.S. Air Force back in 2004, after 40 years of Navy control.
In 2014, construction finally began, with Lockheed Martin as the prime contractor, and General Dynamics and AMEC assisting. The primary base location is located at PPF9+CG7, Kwajalein Atoll, Marshall Islands. Lockheed Martin had put together a theatrical 6-min video on Space Fence about the imminent threat of debris to America’s Space assets and how Space Fence will revolutionize Space situational awareness with assured surveillance coverage. On March 27, 2020, the U.S. Space Force declared the $1.5 billion Space Fence infrastructure to be operational.
According to Lockheed Martin’s web page, Space Fence “provides uncued detection, tracking and accurate measurement of space objects, including satellites and orbital debris, primarily in low-earth orbit (LEO)…It also significantly improves the timelines with which operators can detect space events.” It can detect objects as small as a marble and provide cover in geosynchronous orbit all while maintaining a surveillance fence.
Space Fence isn’t just for tracking debris. The 20th Space Surveillance Squadron at Eglin Air Force Base makes up a 250-member squadron that conducts around the clock command and control operations of two weapon systems: the phased array radar and Space Fence.
A second Space Fence station was to be built in western Australia, but there has been no mention of that construction or funding. In 2021, Lt. Gen. Stephen Whiting, head of Space Operations Command, spoke out about the need for the second station, as they were currently tracking over 35,000 space objects. He had also said that a new program was being developed called the “Deep Space Advanced Radar Capability(DARC),” which could handle some of the capabilities the second Space Fence could provide. “The DARC system will affordably field an advanced, 24/7 all-weather capabilities, not supported in any existing ground-based radar,” Whiting stated. This new system is supposed to be operational in 2025, along with two additional sites planned.
For additional photos, diagrams, and information pertaining to Space Fence, the eoPortal is a site supported by the European Space Agency that covers space related topics and endeavors, including Space Fence – with no endorsement by Corey’s Digs as to the validity of content.
Companies and defense contractors are also working on space-tracking systems. For example, LeoLabs, a Silicon Valley company founded in 2016 to track satellites and orbital debris, has already setup six operation radar sites in Alaska, Texas, Costa Rica, Australia, and two in Azores Archipelago, with a goal to install radars in 24 locations worldwide. They recently announced a partnership with U.S. defense contractor SAIC to build a space-tracking software platform.
As of October 1, 2023, the U.S. Army’s Joint Tactical Ground Station Missile warning system officially transferred to the U.S. Space Force, following the transfer of the Army’s Satellite Communications back in August 2022. JTAGS process satellite data and disseminate ballistic missile warnings. For the first time ever, all military SATCOM capabilities were consolidated under one service and transferred 200 civilians and 300 military personnel from the Army to the Space Force, with the 53rd Space Operations Squadron in charge under Delta 8.
Space Force is currently in the process of drafting up “guidelines” for the use of commercial satellites to integrate them into military activities. This “soon to be released commercial space strategy” involves the U.S. military relying on commercial companies during peacetime and wartime. “My hope is that this will bring some clarity to the industry so that they can globally support and augment inherently governmental and military activities that we project from the space domain,” explained U.S. Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman.
I wanted to glean a little more insight into Space Fence and other activities taking place in our atmosphere, so I reached out to the extraordinary writer and researcher Elena Freeland, who has published numerous books on Space Fence, chemtrails, electromagnetics, nanotechnology, HAARP, geoengineering, transhumanism, full spectrum dominance, and the Deep State, showing how the environment has been weaponized against us.
Elena Freeland’s second book titled Under an Ionized Sky: From Chemtrails to Space Fence Lockdown is very important because it’s about how to weaponize an entire electromagnetic system in order to run the earth as a machine.
As Freeland began explaining actions and probable goals with these mechanisms, based on decades of research, she stated that “the idea is that the human mind is to be plugged into the Secret Space Program and of course the Space Fence.” She went on to say that “Lockheed Martin is number one in the world for arms sales and is the one that owns all the patents, to my knowledge, for the Space Fence.” In regards to Space Fence, she said that “it’s like turning your devices into nodes on the smart grid.” Freeland believes that they completely own the ionosphere and have control of the magnetosphere, and achieved this by 2013 because of HAARP. She also believes that the Schumann resonance is being adjusted by the same people who have this control.
In Freeland’s second book, she began with explaining Operation Cloverleaf which utilized the HAARP system in conjunction with particulate matter that had to be in the sky in order to be able to run all of the wireless programs they needed to run.
This may sound a little crazy to those just now learning about weather manipulation and other technologies the U.S. has been utilizing for years, but there is ample documentation on this. In a 1996 paper titled Weather as a Force Multiplier: Owning the Weather in 2025 for the U.S. Air Force, they have a section designated specifically to “Communications Dominance via Ionospheric Modification,” not to mention, “Artificial Weather.”
The report states, “In 2025, US aerospace forces can own the weather by capitalizing on emerging technologies and focusing development of those technologies to war fighting applications. Such a capability offers the war fighter tools to shape the battlespace in ways never before possible. It provides opportunities to impact operations across the full spectrum of conflict and is pertinent to all possible futures…The technology is there, waiting for us to pull it all together. In 2025 we can ‘Own the Weather’…In 1957, the president’s advisory committee on weather control explicitly recognized
the military potential of weather-modification, warning in their report that it could become a more important weapon than the atom bomb.”
In the article by Amy Worthington on Global Research, titled “Chemtrails: Aerosol and Electromagnetic Weapons in the Age of Nuclear War” from 2004, it provides information on numerous operations and weapons along with over 90 cited sources. It gets into weapons by frequencies, plasma, electromagnetic, sonic, ultrasonic, laser, chemical, environmental, electronic, and more, and explains how it all directly ties into capabilities via Space.
We briefly discussed CERN and their obsession with the magnetosphere, electromagnetic grid on earth, and satanic rituals around opening up other dimensions, which Corey’s Digs has reported on. It should be noted that CERN also has immunities.
Freeland’s biggest concern seemed to be about nanotechnology, stating that “the nanotech is the sealant of all of this. This nanotech is actually another Manhattan project because it takes place on the atomic level – laying atom next to atom next to atom….The nano part is the most mysterious and most dangerous to our species because now they’ve got it in the serums and jab everybody and get more nanotech into them, but we all have nanotech because we’ve been breathing it for 25 years. And so, it’s the nanotech that will be the real nodes, in a way, that plug the human being deeply into the secret space programs that come out of the Space Fence lockdown.”
In a Corey’s Digs report by The Sharp Edge, she reported that in 2021, the White House ‘National Nanotechnology Initiative Strategic Plan,’ emphasized the critical importance of developing nanotechnology to fuel progress in areas such as drug delivery systems, noting the success of using nanomaterials in the Covid injections and “new efforts to develop nanoparticle ‘universal’ vaccines,” while also acknowledging the contributions of nanotech in advancing quantum computing and artificial intelligence.
Freeland and I continued our conversation…
Lynn: And so the digital ID is nothing more than a hall pass.
Freeland: Yes. Then the global village has battle space, I call it, and this concept of the smart cities and 15 minute cities, these are definite nodes being defined for the battle space. And you might wonder, battle space with who? It’s with the humans versus those who despise humanity, ie: satanists.
Up there, let’s think of it as Elon Musk’s Neuralink. Let’s think of it as a mesh, a grid and there are all kinds of energy systems that are producing, including the sun, producing the energy lines that one needs in order to have that as the canopy of operation. Then we’ve got the backup of the lasers. And as far as satellites…as I understand it from Arthur Firstenberg, he mentioned the quantity of I believe 175,000 satellites are up there. (I looked it up, and the quantity is 441,449 for satellites that are either operating, approved, or proposed as of January 2022. See full breakdown here. Firstenberg is on Substack here.)
The satellite is playing quite a role here. If we look at the satellite, and say we got a map around the earth… I think you would see that grid I’m talking about. Around the circumference of the earth are tons and tons of heavy metal particulates that are making an antenna around the earth, much like Saturns rings. That’s going to be very key. That’s for communications… everything is about space and about being Gods and running this solar system.
Lynn: In regards to the space-based solar systems, do you think that’s merely a cover story and they don’t plan to beam anything down at all or do you actually think they are going to be beaming something destructive toward us?
Freeland: I’m assuming they’ve got a variety of things. The main thing they are most interested in, and this is very interesting, is the plasma, because the sun of course is made of plasma, and they are doing mass experiments in our atmosphere with plasma. All those clouds that we see above us, those are all plasma clouds, those are not natural clouds – not the way they used to be. They are not filled with moisture by any way, shape or form, because they need dry atmosphere for communications, and communications include the whole C5ISR.
Lynn: So you are saying that moisture in the air will mess with their signals?
Freeland: Yes, communications will not be good. They’ve got to have it dry for all of their operations.
Lynn: That’s why we are dealing with drought and bad soil and all of this stuff.
Freeland: Yes.
We concluded our conversation agreeing on the point that a higher consciousness is needed to battle these fronts and that self healing and protections are viable for those who do the work. Freeland insists that no one should have a television or smart phone because they are ultimately weapons.
In a Corey’s Digs report by The Sharp Edge, it breaks down the funding going into some of the tech talked about above, as well as advancements already made. This is just a short segment from this in depth report:
Rapid advancements in biotech, nanotech, and brain-computer interface have taken place over the past few years. In a prescient discussion on “Neurobiology and War” at West Point in 2018, Dr. Charles Morgan, who previously worked for the CIA, discussed the future of warfare within 5 years, given the developments of emerging technologies in the arenas of biotech, nanotech and human-machine interface. Morgan discussed the weaponization of gene editing CRISPR technology to program cells to kill specific people or induce memory loss, as well as the use of designer drugs, known as DREADDS, that can be remotely controlled when the brain is exposed to electromagnetic stimulation. (As a side note, remote control of the behavioral responses in test subjects can be achieved by using injected magnetic nanomaterials in conjunction with magnetic field manipulation, according to one recent study.) Additionally, Morgan presented “the new way to hide information” through technological developments in DNA encryption, by which one gram of DNA is capable of storing 700 terabytes of information. Morgan also discussed the use of brain-computer interface systems by the military and intelligence communities to “co-opt” the bodies of people in other parts of the world, to transfer thoughts and communications from human to human, to exploit biological species to become drones for spying, as well as to create a “hive brain” among a group of people.
The U.S. 2022 Omnibus and NDAA funded nearly $7 billion toward these technological and scientific areas. Additionally, the Pentagon released an Electromagnetic Spectrum Superiority Strategy in 2020, with implementations of the strategy the following year. The EMS strategy includes advanced capabilities in Directed Energy Weapons (DEW). The DOD more than doubled spending on directed energy weapons from $535 million in 2017 to $1.1 billion by 2019. By 2022, appropriations for directed energy research and development reached $745 million plus an additional $325 million for directed energy weapons procurement.
The Safe Zone: Space Laws
The framework of global space governance is broken down into four areas: UN space treaties, UN voluntary guidelines, bilateral / multilateral agreements, and national / state laws.
UN Space Treaties
The “Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty,” prohibits nuclear weapons testing under water, in the atmosphere or in space.
The “Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies,” referred to as the Outer Space Treaty or OST, includes: the use of space for peaceful purposes, bans appropriation of space or celestial bodies, prohibits weapons of mass destruction in space or on celestial bodies, considers all astronauts as envoys of mankind, and requires states to supervise their nations’ space activities.
The “The Agreement on the Rescue of Astronauts, the Return of Astronauts, and the Return of Objects Launched into Outer Space,” known as the Rescue Agreement, requires states to rescue astronauts during accidents or emergency landings and return astronauts and space objects to their state of origin.
The “Convention on International Liability for Damage Caused by Space Objects,” known as the Liability Convention, breaks down the liability of states for damages created by space objects and outlines the procedures for settling claims.
The “Convention on Registration of Objects Launched into Outer Space,” referred to as the Registration Convention, requires states to maintain a registry of their space objects and submit data to the UN regarding the objects launched into space.
The “The Agreement Governing the Activities of States on the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies,” known as the Moon Treaty, which was not signed by the U.S., Russia, China or the European Space Agency, requires the Moon to be used for peaceful purposes and bans weapons of mass destruction, weapons testing, or military installations on the Moon.
UN Voluntary International Guidelines – These guidelines are non-binding and voluntary
The “Declaration of Legal Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space” outlines the legality of space activities.
The “Declaration of Guiding Principles on the Use of Satellite Broadcasting for the Free Flow of Information, the Spread of Education and Greater Cultural Exchange,” provides principles for the use of satellite broadcasting to benefit all countries.
The “Principles Relating to Remote Sensing of the Earth from Outer Space,” provides principles for using remote sensing for the benefit of all countries.
The “Principles Relevant to the Use of Nuclear Power Sources in Outer Space,” provides guidelines for nuclear power sources in outer space to reduce radioactive material and associated risks.
The “Declaration on International Cooperation in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space for the Benefit and in the Interest of All States, Taking into Particular Account the Needs of Developing Countries,” encourages international cooperation on space exploration programs.
Bilateral and Multilateral Space Agreements
There are many bilateral and multilateral agreements between countries on joint space activities, some of which can be found here.
The “Artemis Accords,” is a multilateral agreement including the U.S. on a set of principles that focuses on shared cooperation in exploration and extraction of resources on the Moon, Mars, comets and asteroids.
U.S. Legislation
The “National Aeronautics and Space Act of 1958,” known as the NAS Act, placed control of U.S. space activities under NASA with the exception of weapons development and military operations which is controlled by the DOD.
The “Communications Satellite Act of 1962,” known as the Comsat Act, authorized U.S. participation in an international cooperation agreement on a satellite communications network known as Intelsat. In 2000, the Orbit Act was passed which transformed Intelsat into a private for-profit company. (See key dates and info on this under the Satellites section above)
“Title 51 – National and Commercial Space Programs,” governs NASA, scientific research related to space, commercial activity, remote sensing, and the International Space Station.
The “National Aeronautics and Space Administration Authorization Act of 2010,” focuses on human spaceflight programs, the International Space Station, and commercial space transport of cargo and humans to the ISS.
The “U.S. Space Launch Competitiveness Act,” authorizes the commercial recovery, possession, use, and sale of asteroid and space resources.
The National Defense Authorization Act of 2019 established Space Force, a new branch of the U.S. military, to maintain space superiority in orbital warfare, space electromagnetic warfare, space battle management, space access and sustainment, military Intelligence, cyber operations, and engineering and acquisitions.
Several U.S. states listed here have enacted laws to encourage commercial space activity.
These treaties with “agreements” and “volunteer guidelines” all seem like a farce. First off, anything drafted up through the UN means that all internal documents and bank records are inviolable. They have layers and layers of immunities and privileges that nearly exceed that of a diplomatic immunity. Thanks to the heads of countries dating back to 1945, they have been operating entirely outside the law ever since. Read Corey’s Digs in depth report on this here.
Second, all U.S. legislation is merely there for the benefit of the government and those in the shadow government. It does nothing to protect citizens. It advances their agenda, commercializes space with satellites, space stations, mining, objects, and more.
Third, despite these treaties and agreements, countries have not been abiding by them and there is obvious conflict between countries, as well as a space race taking place.
Will there be any oversight, transparency, enforcement, or protections for civilians when it comes to surveillance, weapons, control through technology, financial infrastructure, privacy and data? It is highly unlikely. Is this the ultimate off-shore haven for the corrupt? It sure seems that way.
Matthew R Hale Attorney at Law wrote an article pertaining to space law for the Solari Report in 2020. It’s definitely worth the read, as it breaks down laws in a handful of other countries and gives more background on some of the legislation, treaties, and accords.
Giant Leap: Digital Currency Moving Faster Than a Rocket
“Fast Payment Systems” (FPS) are moving “fast” through over 60 countries, the FedNow gateway is up and running, the cross-border gateway test has already succeeded through BIS, numerous countries are piloting digital currencies, ISO standards changed this year to add more data, blockchain and crypto have launched to Space, CBDCs are everyone’s focus but not immediately necessary to lock in their plan, and the battle is on for the future of global currency.
In order to keep this section short while providing the necessary receipts, below is a consolidated bullet point breakdown on how quickly things are moving, by combining research, past reports on Corey’s Digs, and an excellent breakdown by Coin Bureau. A short recap follows.
• In this 2022 Bank for International Settlements (BIS)report they make a very significant statement on page 13:
“It needs to be noted that many of these features can, in isolation, be offered by other payment innovations, and many gaps could be addressed through regulation and sound oversight arrangements.” CBDC’s may not be necessary because “combining different payment innovations such as open application programming interfaces (APIs), fast payment services, contactless chips and QR codes could achieve many of the same goals.” They go on to state, “This is particularly true when accompanied by robust regulatory and oversight arrangements that public authorities can use to catalyse private sector players, enforce sound governance arrangements and foster required coordination and collaboration.”
They sum it up with this: “What is truly different about CBDC is that it is a direct claim on the central bank. It is an open question for central banks whether CBDCs or other policy interventions are the best fit for their jurisdiction. Yet if a CBDC is to be issued (for financial inclusion or other motives), interviews with central banks clearly point to the importance of inclusive design elements to successfully promote inclusive outcomes,” and follow it up with a section on interviews with central banks.
• In a separate 2022 BIS report, they state that they intend to develop an international CBDC system that will be in sync with the Fast Payment Systems (FPS). More on FPS below.
• In a 2021 World Bank report, they state that a “CBDC network and a fast payments network do not necessarily have to compete. One potential option in this space would be using a CBDC as a settlement currency for a fast payment system. This may be particularly attractive in a cross-border context, where settlement risk is high today due to slow and inefficient processes for cross-border payments.”
And in a separate report by the World Bank that same year, specific to cross-border Fast Payments, they explained that “any stakeholders developing a cross-border FPS should account for the introduction and expansion of CBDC to determine the feasibility of including CBDC in a cross-border FPS arrangement. This includes the development of flexible interfaces (for example, using APIs) as part of a cross-border FPS arrangement that would allow for a future linkage with a CBDC network(s).”
• Currently, over 60 countries have a FPS in place, and several others have announced their plans to go live. According to the World Bank, “the basic principle among all the countries remains the same — that is, to provide a real-time, 24/7 fund-transfer facility.” The progress and specifics of the FPS systems in each country can be tracked on the World Bank’s global tracker.
The World Bank began running test programs and studies with banks and later published their preliminary analysis of global developments in 2020 with an emphasis on how the “pandemic” played such an important role in the need for FPS, then in 2021 put out a press release announcing the soon-to-be-launched toolkit for their new Fast Payment Systems (FPS) to assist countries with getting on board. Guess who helped out with this endeavor?
“This project would not have been possible without the generous support of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation and the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The support is provided through the Financial Inclusion Support Framework program.”
The Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation granted $9.2 million to the World Bank for “accelerating adoption of fast payment systems in low-income countries” in September 2022. Bill Gates is a front man with three big tax exempt organizations that the corrupt move their money through. They need him to be the target so eyes aren’t on them.
• In 2017, The Clearing House created the real-time payments (RTP) platform for all federally insured U.S. depository institutions. This allowed for the instant electronic transfer of money between banks in the U.S. A similar system exists in 176 countries. Whereas, with Fast Payment Systems (FPS), the instant settlement of funds takes place for both the payer and payee. This involves moving money through online banking or third parties via mobile applications, some of which also integrate QR codes.
Non-banks can participate by connecting to the central infrastructure of the FPS by signing an agreement with a sponsor bank that settles their transactions at the RTGS system. Since the RTP network allows third parties to enable proxy payments, PayPal and Venmo are already connected, and TCH has partnered with Zelle to provide settlement payments. Rules, payment arrangements and access criteria vary by country. A more in depth explanation of this, as well as some country specific details, can be found here.
In the World Bank’s report, they talk about how biometric authentication by customers provides superior security and how it’s becoming increasingly common.
• Incorporating QR codes (scan-to-pay) is a goal to get more people to adopt using FPS. The Federal Reserve has a page dedicated to how great QR codes are. The “Faster Payments Council” (FPC) has also created a page dedicated to utilizing QR codes for “faster payments,” stating that China has increased their use of QR codes 15-fold, reaching $1.3 trillion U.S. in the fourth quarter of 2019. They go on to explain how QR codes are going to take off and check all the boxes for providing an easy interface, offering a layer of tokenization, and “take advantage of an existing consumer understanding of the technology.”
The FPC produced a 19-page white paper on QR codes for faster payments in July 2022. They want a “standardized certification program covering all major mobile devices and operating systems” and “extensible standards with the ability to offer value-added services such as merchant offers, coupons and tokenization.”
For these reasons, the FPC formed the End-User QR Code Interface Work Group, chaired by Walmart’s Matt Howarter. Walmart was one of the early adopters of payment via QR code. They implemented Walmart Pay years ago. This article gives a good breakdown on the history of QR code use in the U.S. and some other countries.
• The Faster Payments Council also has a bi-monthly podcast called “Off the Rails from the U.S. Faster Payments” for those who wish to follow their updates.
• In the 2021 Fast Payment Systems report by the World Bank, they talked about Crypto assets, stating that “crypto assets appear to be on the rise globally, including some that certain individuals and firms consider to be a medium of exchange. If these crypto assets with payment capabilities gain more mainstream acceptance, a question will arise as to whether or how they shall or could become interoperable with existing payment systems, including fast payment arrangements.”
The Coin Bureau points out the significance of this for both the cryptos that are already interoperable with the ISO 20022 standard and other cryptos because central banks could replace stablecoins with fast payment systems and CBDCs, which means crypto prices would be controlled, and go on to suggest that a decentralized stablecoin needs to be built asap.
In an August 22, 2023 report on BIS’ site titled ‘Financial stability risks from cryptoassets in emerging market economies‘, BIS sheds more light on this, concluding that “Authorities face a number of policy options to address risks in crypto assets, ranging from outright bans to containment to regulation. Bans and containment – if they are effective – may prevent financial stability risks from arising. At the same time, there are risks if central banks and regulators react in an excessively prohibitive manner. For instance, activities may be driven into the shadows, and it may be more difficult to influence responsible actors in the sector. More generally, new approaches should not be automatically classified as ‘dangerous’ simply because they are different. Responsible innovation, technology and new players can reduce frictions and inefficiencies in payment systems and lower barriers to entry. Throughout history, technology has been key to driving improvement and increasing the resilience of financial services. While crypto-related activities have not fulfilled their stated goals to date, the technology could still be applied in various constructive ways. Creating a regulatory framework to channel innovation into such socially useful directions will remain a key challenge in the future.”
Also covered in this report, they state “Recently, the industry has been giving more thought to how this technology could be integrated with Fast Payments. For example, some players in the industry believe that connecting the latter to existing distributed ledgers would facilitate programmable Fast Payments.”
This is where the QR codes come into play. If this technology can be programmable, that means central banks can control what you buy, not to mention governments. This was covered in depth in the book titled The Global Landscape on Vaccine ID Passports, by Corey Lynn.
• FedNow is the new instant payment infrastructure created by the Federal Reserve that launched this year. They kicked off with 35 early-adopting banks and credit unions, as well as the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Bureau of the Fiscal Service, and over a dozen service providers. This adds yet another gateway or “rail” for moving funds through banks quickly.
The Federal Reserve is using Swift’s MyStandards platform to provide access to the FedNow ISO 20022 message specifications.
• The messaging standards report talks about ISO 20022. It’s international and interoperable which was first developed in 2004 and was set to launch in November 2022, but didn’t go live until March 2023. In another words, this standard in financial messaging was created nearly two decades ago with a target date of 2022.
The most widely promoted advantage of ISO 20022 is data. “Each data element is highly structured and is defined in the same way, not just in payments but across any use, whether capital markets, cards, or e-invoicing…the format can support both structured and unstructured data, and considerably more data at that.”
Banks and corporations are briskly working to get everything moved over, with a 2025 deadline on the horizon.
Most of the 60 countries using FPS are already compliant with ISO 20022 standards.
• The BIS Innovation Hub is in its fourth year, with five concluded projects and 21 in the works, with 15 of the 26 projects focused on CBDCs. They’ve been very busy. One particular project called Nexus focuses on cross-border payments with the ability to connect all of the Fast Payment Systems so countries can add the Nexus gateway. They ran a 12-month proof of concept between the Eurosystem, Malaysia and Singapore to show how Nexus can accelerate the growth of instant cross-border payments. In their 2023 report they stated that this “opens the door to other alternative payments infrastructure, such as CBDCs, to connect to Nexus.” This was followed up with a report on September 28, 2023 showing the successful test on cross-border wholesale CBDCs that was tested through BIS and central banks of France, Singapore and Switzerland. They state that “this could form the basis for a new generation of financial market infrastructures.”
To recap, BIS, Central Banks and financial institutions, the World Bank, Federal Reserve, and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (front) have been very busy rolling out a digital financial plan for the near future. They’ve made great strides while many distractions have been taking place to keep everyone’s focus off it. In fact, the FedNow gateway that rolled out at 35 major bank chains have been testing their gateway for months, unknowingly to most consumers. Banks even state that the consumer doesn’t need to worry about which rail their money sails through, because the bank will choose the best one for them. Isn’t that wonderful? So just imagine when other gateways and networks are formed. Most people will only recognize that their money was sent or arrived quicker than before, “somehow.” Meanwhile, J.P. Morgan, Bitcoin, and others are already working on transacting via space through blockchain. With BIS at the helm, diligently working on Nexus and CBDCs, it seems only a matter of time before banks piggyback the Fast Payment Systems over to CBDCs with biometric authentication and QR codes. How soon will all of these transactions be bouncing from satellite to satellite up in space? Does anyone truly believe that a “decentralized” blockchain is going to really be “decentralized?”
T-minus
Can you see it now?
This report is not meant to invoke fear, but rather make people aware of what these groups (covered extensively throughout Corey’s Digs reports) are up to so that people have some level of advance knowledge in the hopes to prepare accordingly and potentially derail some of their plans.
It is clear that there is both a Space race and digital currency race taking place simultaneously. Whereas, they don’t need the CBDCs in place to lock in the control mechanisms, they intend to piggyback it on to the Fast Payment Systems and already have it pretty well set to go once they have the green light. Cryptocurrencies are also getting in on the action, but may face regulations and oversight soon enough. Digital wallets seem to be holding their own and some are working on necessary updates with banks as these systems continue to evolve, so as to maintain their position. It is also evident that they still intend to use the banks to drive QR codes and biometrics, which will ultimately act as the Digital ID or “hall pass.” One day, all payments will run through smart contracts via smart phones that send and receive tokens through blockchain pinging down from a satellite, and brick and mortar banks may no longer exist. Being as satellites have laser beams creating a mesh network in Space, it probably won’t be long before their main earth-based stations become obsolete, perhaps leaving simple receiver dishes on homes and the over 400,000 cell sites already flooding the country.
The Space Military Industrial Complex is in high gear, with a lot more responsibilities being transferred over to Space Force. The U.S. and other countries have committed a lot of money to building out infrastructure and loading the skies with satellites and surveillance systems. Though they all have common goals, there is definitely competition. The level of weaponry and control mechanisms already in place is evidence that they aren’t messing around.
Based on white papers, funding, executive orders, and documents pertaining to nanotechnology, biosecurity, brain chips, and the ability to transfer thoughts and communications from human to human through tech, the transhumanism agenda seems more and more plausible by the day. Robots and AI are destined for our future based on the speed at which they are rolling out machine learning and other tech.
Taking into account all of the information in this report, and much that didn’t even make it into the report, it is my opinion that they are building the main central operations for the control grid in Space, equipped with full blown surveillance, nodes throughout every city, data centers, the internet, solar systems to power satellites and data centers, a suite of weaponry, a blockchain-based financial infrastructure, and likely equipping cell phones with additional hardware and software that has biometrics and integrates better with their satellite surveillance system. It’s all very clever. The biggest reason I believe this to be the case is because of the location. Most of these corrupt people have been operating outside the law since 1945, so why not go entirely outside the playing field to a place that has no laws, transparency, or oversight – only “agreements” that they do not abide by? Why not be the ultimate eye in the sky with a bird’s eye view of their masterful control grid, trying to run everyone like puppets? It just makes sense.
I’m always asked, “how do we stop this?” I don’t think we can stop all of it, but perhaps some of it. I believe the digital currency is moving forward with such fervor that it will be a difficult one to derail. Some folks may feel there is a way to utilize it to our advantage and decentralize it, but I cannot see a clear path to that. It’s not my area of expertise. Nonetheless, I will continue to use cash for nearly everything. On that note, I refuse to support corrupt organizations fueling our enslavement, so I personally shop here for all of my main necessities and never ever mRNA beef. I also have a great resource for finding sources of fresh food and local farmers, plus lots of solutions here and here on a wide range of subjects. Obviously, ditching smartphones is a “smart” move since it’s a surveillance weapon and beyond. That said, if it’s not done by a high volume of people, it could one day pose a problem with being able to access funds or make transactions. I am not suggesting to keep one based on that, I’m just pointing out the facts. I believe that everything we do to not comply with tyrants makes an impact, getting out important information is critical, and above all – moving to a higher consciousness and recognizing our true innate power and the ability we have to manifest the reality we want for our future – is by far the most powerful took in our toolbox.
This report is sponsored by The Solari Report.
Related Reading:
Sky’s The Limit for Globalists’ Boiling Earth Narrative, Corey’s Digs
Laundering with Immunity: The Control Framework – Part 1, Corey’s Digs
Geoengineering, the Space Fence, and the Advent of Transhumanism, The Solari Report
The Space Race with Elze van Hamelen, The Solari Report
Issues and Framework of U.S. Law Concerning Outer Space, The Solari Report
BIS Blueprint = Global Control of ALL Assets, Information & People , Corey’s Digs
Funding The Control Grid Part 4: The Technology Framework, Corey’s Digs
The Rise & Risks of Central Bank Digital Currencies, Corey’s Digs
Source: Spaceforce.mil
Space Force announces Integrated Mission Delta construct to optimize for Great Power Competition
Published Sept. 12, 2023
By SAF/PA Staff Writer
Secretary of the Air Force Public Affairs
NATIONAL HARBOR, Md. --
U.S. Space Force Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman announced two new Integrated Mission Delta provisional units, scheduled to activate in Fall 2023.
IMDs will integrate resources around mission areas (e.g., satellite communication; positioning, navigation, and timing, electronic warfare, missile warning) instead of the traditional functional model (e.g., operations, acquisitions, intelligence, cyber effects) in place today. This new command structure will organize all aspects of mission area readiness – personnel, training, equipment, and sustainment – into a single organization.
The first two provisional IMD units will support electromagnetic warfare and positioning, navigation, and timing mission areas and align under Space Operations Command. These IMDs will combine force elements in Space Operations Command that perform mission generation, intelligence support, and cyber defense with program offices in Space Systems Command that oversea maintenance activities.
“Performance should be optimized around our missions rather than the functions that support them; we cannot afford to split a mission area’s critical activities across organizational seams,” Saltzman said. “It is essential that all elements of readiness - people, training, equipment and sustainment - fall into the same organizational structure, and that we create unity of command around those elements at the lowest possible level.”
This announcement comes after Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall’s comments in a recent memo to the Department for the need to optimize the force to address the current strategic environment.
“Over more than two decades, we have optimized to support post-9/11 conflicts and demands; this is not what the nation needs for the coming decades of strategic competition,” Kendall stated in the memo.
Prototyping of IMDs is part of the Space Force’s effort to transition from simply establishing a new service to forging a service purpose built for great power competition. The goal is to create unity of command for readiness while also streamlining unity of effort for capability development.
“We are going back to basics and creating the structure and processes we will need to be successful in this new era.” Saltzman said.
This concept will be thoroughly evaluated and refined before it is considered for implementation across the force. This initial effort will not involve the physical relocation of personnel and it will not change the core missions of SpOC or SSC.
Ways to connect
Telegram: @JoelWalbert
Email: thetruthaddict@tutanota.com
The Truth Addict Telegram channel
Hard Truth Soldier chat on Telegram
Mastodon: @thetruthaddict@noagendasocial.com
Session: 05e7fa1d9e7dcae8512eed0702531272de14a7f1e392591432551a336feb48357c
Odysee: TruthAddict
Donations (#Value4Value)
Buy Me a Coffee (One time donations as low as $1)
Bitcoin:
bc1qe8enf89g667dy890j2lnt637xqlt9wvc9f07un (on chain)
nemesis@getalby.com (lightning)
joelw@fountain.fm (lightning)
+wildviolet72C (PayNym)
Monero:
43E8i7Pzv1APDJJPEuNnQAV914RqzbNae15UKKurntVhbeTznmXr1P3GYzK9mMDnVR8C1fd8VRbzEf1iYuL3La3q7pcNmeN